Create, Import, and Configure AUTOSAR Computation Methods
AUTOSAR software components use computation methods (COMPU-METHOD) to
convert between the internal values and physical representation of AUTOSAR data.
Embedded Coder® imports AUTOSAR COMPU-METHODs described in ARXML code and
preserves them across round-trips between an AUTOSAR authoring tool (AAT) and Simulink®. In Simulink, you can modify imported computation methods or create and configure new
computation methods.
This topic provides examples of configuring AUTOSAR computation methods in Simulink.
Create AUTOSAR Computation Methods
You can create AUTOSAR computation methods in your model, either graphically or
programmatically. To create an AUTOSAR computation method using the graphical interface,
open the AUTOSAR Dictionary and select the CompuMethods view. To
open the Add CompuMethod dialog box, click the Add button
![]() . Configure the initial properties for the computation
method, such as name, category, unit, display format for calibration, AUTOSAR package to
generate, and associated Simulink data type. When you click OK, the CompuMethods view
in the AUTOSAR Dictionary is updated with the new computation method.
. Configure the initial properties for the computation
method, such as name, category, unit, display format for calibration, AUTOSAR package to
generate, and associated Simulink data type. When you click OK, the CompuMethods view
in the AUTOSAR Dictionary is updated with the new computation method.

Note
You cannot create COMPU-METHOD categories
BITFIELD_TEXTTABLE and
SCALE_LINEAR_AND_TEXTTABLE from the AUTOSAR
Dictionary.
When you generate code, the exported ARXML code contains the
COMPU-METHOD definition and references to it.
Import AUTOSAR Computation Methods
You can import AUTOSAR COMPU-METHOD categories
IDENTICAL, LINEAR,
TEXTTABLE, BITFIELD_TEXTTABLE,
SCALE_LINEAR_AND_TEXTTABLE from ARXML. To import an ARXML file
use the arxml.importer object, and create a model from its contents using the
createComponentAsModel function.
ar = arxml.importer("Gears_States.arxml")ar =
The file "C:\work\Gears_States.arxml" contains:
1 Application-Software-Component-Type:
'/SwComponentTypes/SWC'createComponentAsModel(ar,"/SwComponentTypes/SWC");The imported computation methods can be accessed and edited from the AUTOSAR Dictionary.
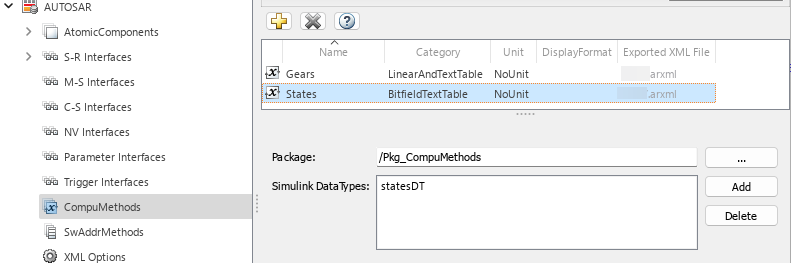
The computation method States of category
BITFIELD_TEXTTABLE is used in sender receiver communication for
the component. The elements (ShortLabel, Mask,
LiteralValues, and LiteralText) of the
computation method are defined by COMPU-SCALES in the ARXML.
<AR-PACKAGE>
<SHORT-NAME>Pkg_CompuMethods</SHORT-NAME>
<ELEMENTS>
<COMPU-METHOD UUID="...">
<SHORT-NAME>States</SHORT-NAME>
<CATEGORY>BITFIELD_TEXTTABLE</CATEGORY>
<COMPU-INTERNAL-TO-PHYS>
<COMPU-SCALES>
<COMPU-SCALE>
<SHORT-LABEL>Problem</SHORT-LABEL>
<SYMBOL>ProblemNone</SYMBOL>
<MASK>255</MASK>
<LOWER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000000000</LOWER-LIMIT>
<UPPER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000000000</UPPER-LIMIT>
</COMPU-SCALE>
<COMPU-SCALE>
<SHORT-LABEL>Problem</SHORT-LABEL>
<SYMBOL>ProblemFailure</SYMBOL>
<MASK>255</MASK>
<LOWER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000001000</LOWER-LIMIT>
<UPPER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000001000</UPPER-LIMIT>
</COMPU-SCALE>
<COMPU-SCALE>
<SHORT-LABEL>Problem</SHORT-LABEL>
<SYMBOL>ProblemMajor</SYMBOL>
<MASK>255</MASK>
<LOWER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000011000</LOWER-LIMIT>
<UPPER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000011000</UPPER-LIMIT>
</COMPU-SCALE>
<COMPU-SCALE>
<SHORT-LABEL>Problem</SHORT-LABEL>
<SYMBOL>ProblemAll</SYMBOL>
<MASK>255</MASK>
<LOWER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000111000</LOWER-LIMIT>
<UPPER-LIMIT INTERVAL-TYPE="CLOSED">0b0000000000111000</UPPER-LIMIT>
</COMPU-SCALE>
</COMPU-SCALES>
</COMPU-INTERNAL-TO-PHYS>
</COMPU-METHOD>createEnumeration function.arProps = autosar.api.getAUTOSARProperties(modelName);
createEnumeration(arProps,'/Pkg_CompuMethods/States');This creates States_defineIntEnumTypes.m which, when run, recreates
the enumeration types in Simulink. This captures the properties of the BitFieldTextTable
COMPU-METHOD and allows them to be used by software components in
Bitwise Operator or Relational Operator blocks.
Configure AUTOSAR Computation Methods Properties
You can configure AUTOSAR computation method properties in your model, either graphically or programmatically. You can modify computation method properties: name, category, unit, display format, AUTOSAR package, and Simulink data types.
To configure a computation method using the graphical interface, open the AUTOSAR Dictionary and select the CompuMethods view. This view displays the modifiable computation methods in the model, whether imported from ARXML code or created in Simulink.

Select a computation method and edit the available fields.
Name — Specify name text
Category — Select
Identical,Linear,TextTableUnit — Select from units available in the model
DisplayFormat — Optionally specify format to be used by calibration and measurement tools to display the data. Use an ANSI® C
printfformat specifier string. For example,%2.1dspecifies a signed decimal number, with a minimum width of two characters and maximum precision of one digit. The string produces a displayed value such as12.2. For more information about constructing a format specifier string, see Configure DisplayFormat.Package — Specify path of AUTOSAR package to be generated for computation methods
Simulink DataTypes — Specify list of Simulink data types that reference the computation method
To modify the AUTOSAR package for a computation method, you can do either of the following:
Enter a package path in the Package parameter field.
To open the AUTOSAR Package Browser, click the button to the right of the Package field. Use the browser to navigate to an existing package or create and select a package. When you select a package in the browser and click Apply, the computation method Package parameter value is updated with your selection. For more information about the AUTOSAR Package Browser, see Configure AUTOSAR Package for Component, Interface, CompuMethod, or SwAddrMethod.
To associate a computation method with a Simulink data type used in the model, select a computation method and click the
Add button to the right of Simulink
DataTypes. This action opens a dialog box with a list of available data
types. In the list of values, select a Simulink.NumericType,
Simulink.AliasType, Simulink.ValueType, or enter
the name of a Simulink enumerated type. If you have a data dictionary linked to your model you
can also select architectural data types defined in the Architectural Data section of
the data dictionary. To add the type to the Simulink DataTypes
list, click OK.

To set the Simulink DataTypes property programmatically, open the model and use an AUTOSAR property set function call similar to the following:
arProps = autosar.api.getAUTOSARProperties("cmSpeed");
set(arProps,"/pkg/CompuMethods/RpmCm","SlDataTypes",{"SpeedRpmAdt"});
slTypes = get(arProps,"/pkg/CompuMethods/RpmCm","SlDataTypes")
slTypes =
'SpeedRpmAdt'Configure CompuMethod Direction for Linear Functions
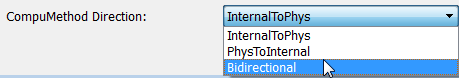
For designs originated in Simulink, you can control properties for an exported computation method (CompuMethod), including the direction of CompuMethod conversion between internal and physical representations of a value. By using either the AUTOSAR Dictionary or the AUTOSAR property set function, you can specify one of the following CompuMethod direction values:
InternalToPhys(default) — Generate CompuMethod sections for conversion of internal values into their physical representations.PhysToInternal— Generate CompuMethod sections for conversion of physical values into their internal representations.Bidirectional— Generate CompuMethod sections for both internal-to-physical and physical-to-internal conversion directions.
To specify CompuMethod direction in the MATLAB® Command Window, use an AUTOSAR property set function call similar to the following:
hModel = "autosar_swc_expfcns_compumethod"; open_system(hModel); arProps=autosar.api.getAUTOSARProperties(hModel); set(arProps,"XmlOptions",CompuMethodDirection="Bidirectional"); get(arProps,"XmlOptions","CompuMethodDirection")
ans = 'Bidirectional'
To specify CompuMethod direction in the AUTOSAR Dictionary, select XML Options. Select a value for parameter CompuMethod Direction. Click Apply.
In this model, an alias data type is defined in linked data dictionary CompuMethodDataTypes and is assigned to an input port of the first runnable subsystem. This data type is used by CompuMethod COMPU_EngSpdValue, and after running the example has a bidirectional CompuMethod direction. In addition to defining and storing data types in the Architectural Data section of data dictionaries, you can also define Simulink data types in the base workspace, and assign them to CompuMethods upon creation.
When you generate code for the autosar_swc_expfcns_compumethod model, the CompuMethods in the exported ARXML code contain the requested directional sections.
<COMPU-METHOD UUID="..."> <SHORT-NAME>COMPU_EngSpdValue</SHORT-NAME> <CATEGORY>LINEAR</CATEGORY> <UNIT-REF DEST="UNIT">/DataTypes/Units/NoUnit</UNIT-REF> <COMPU-INTERNAL-TO-PHYS> <COMPU-SCALES> <COMPU-SCALE> <COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS> <COMPU-NUMERATOR> <V>0</V> <V>1</V> </COMPU-NUMERATOR> <COMPU-DENOMINATOR> <V>1</V> </COMPU-DENOMINATOR> </COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS> </COMPU-SCALE> </COMPU-SCALES> </COMPU-INTERNAL-TO-PHYS> <COMPU-PHYS-TO-INTERNAL> <COMPU-SCALES> <COMPU-SCALE> <COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS> <COMPU-NUMERATOR> <V>0</V> <V>1</V> </COMPU-NUMERATOR> <COMPU-DENOMINATOR> <V>1</V> </COMPU-DENOMINATOR> </COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS> </COMPU-SCALE> </COMPU-SCALES> </COMPU-PHYS-TO-INTERNAL> </COMPU-METHOD>
In exported ARXML files, CompuMethods of category TEXTTABLE use only CompuMethodDirection InternalToPhys. CompuMethods of category TEXTTABLE are generated for boolean or enumerated data types.
Export Computation Method Unit References
The ARXML importer preserves unit and physical dimension information found in imported computation methods. The software preserves the computation method unit and physical dimension information across round-trips between an AUTOSAR authoring tool (AAT) and Simulink.
For designs originated in Simulink, the exporter generates a unit reference for each computation method. By
convention, each computation method references a unit named NoUnit.
For example, here is a Boolean data type computation method and the
unit it references.
<COMPU-METHOD UUID="...">
<SHORT-NAME>COMPU_Boolean</SHORT-NAME>
<CATEGORY>TEXTTABLE</CATEGORY>
<UNIT-REF DEST="UNIT">/mymodel_pkg/mymodel_dt/NoUnit</UNIT-REF>
...
</COMPU-METHOD>
<UNIT UUID="...">
<SHORT-NAME>NoUnit</SHORT-NAME>
<FACTOR-SI-TO-UNIT>1</FACTOR-SI-TO-UNIT>
<OFFSET-SI-TO-UNIT>0</OFFSET-SI-TO-UNIT>
</UNIT>Providing a unit for each exported computation method helps support calibration and measurement tool use of exported AUTOSAR data.
Modify Linear Scaling for ScaleLinearAndTextTable COMPU-METHOD
You can import and export an AUTOSAR COMPU-METHOD that uses
Linear and TextTable scaling. Importing
application data types that referenceCOMPU-METHOD categories
SCALE_LINEAR_AND_TEXTTABLE creates
Simulink.NumericType or Simulink.AliasType
data objects in the Simulink workspace. In Simulink, you can modify the Linear scaling for the computation
methods. The TextTable scaling is read-only.
For example, here is a computation method with one LINEAR scale and two
TextTable scales.

When you import the COMPU-METHOD into a model, the importer creates a
Simulink.NumericType with linear scaling. To modify the linear
scaling, open the Simulink.NumericType data object and modify its
fields.

For read-only access to the TextTable scaling information, use AUTOSAR
property get function calls similar to the following:
arProps = autosar.api.getAUTOSARProperties('mySWC'); get(arProps,'/simple_ar_package/simple_ar_dt/COMPU_myType','CellOfEnums')
ans =
'SensorError' 'SignalNotAvailable'get(arProps,'/simple_ar_package/simple_ar_dt/COMPU_myType','IntValues')
ans = 350 351
Configure Rational Function Computation Method for Dual-Scaled Parameter
For an AUTOSAR dual-scaled parameter, which stores two scaled values of the same physical
value, the software generates the COMPU-METHOD category
RAT_FUNC. The computation method can be a first-order rational
function.
To configure and generate a dual-scaled parameter:
Open an AUTOSAR model. For the purposes of this example, create a Constant block from which to reference an AUTOSAR dual-scaled parameter. In the model, connect the Constant block to a Simulink outport.
Open the Model Data Editor (on the Modeling tab, click Model Data Editor) and select the Parameters tab. Find the parameter entry for the Constant block. Use the Value column to reference the name of a dual-scaled parameter. This example uses the parameter name
T1Rec.
Create the
T1Recdata object. In the Model Data Editor, to the right of the valueT1Rec, click the action button and select Create.
and select Create.In the Create New Data dialog box, set Value to
AUTOSAR.DualScaledParameterand click Create. AnAUTOSAR.DualScaledParameterdata object appears in the base workspace. The dual-scaled parameter property dialog box opens.Configure the attributes of the dual-scaled parameter
T1Rec. Execute the following MATLAB® code. The code sets up a conversion from an internal calibration time value to a physical frequency (time reciprocal) value.% Conversion from Time to Frequency % F = 1/T % In Other Words F = (0*T + 1)/(1*T+0); T1Rec.CompuMethodName = 'CM3'; %Specify AUTOSAR CompuMethod name T1Rec.DataType ='fixdt(1,32,0.01,0)'; T1Rec.CalToMainCompuNumerator=1; T1Rec.CalToMainCompuDenominator=[1 0]; T1Rec.CalibrationMin = 0.001; T1Rec.CalibrationMax = 1.0; T1Rec.CalibrationValue = 0.1500; T1Rec.CoderInfo.StorageClass = 'Custom'; T1Rec.CoderInfo.Identifier = ''; T1Rec.CoderInfo.CustomStorageClass = 'InternalCalPrm'; T1Rec.CoderInfo.CustomAttributes.PerInstanceBehavior =... 'Parameter shared by all instances of the Software Component'; T1Rec.Description = ''; % T1Rec.Min = []; % T1Rec.Max = []; T1Rec.Unit = ''; T1Rec.CalibrationDocUnits = 'm/s²';
Inspect the property dialog box for the dual-scaled parameter
T1Rec. Here are the main attributes set by the MATLAB code.
Here are the calibration attributes set by the MATLAB code.

If the computation method direction is not already set to bidirectional in the AUTOSAR properties, use the AUTOSAR Dictionary, XML Options view, to set it.
Generate code from the model.
When you generate code from the model, the ARXML exporter generates a
COMPU-METHOD of category RAT_FUNC.
<COMPU-METHOD UUID="...">
<SHORT-NAME>CM3</SHORT-NAME>
<CATEGORY>RAT_FUNC</CATEGORY>
<UNIT-REF DEST="UNIT">/mymodel_pkg/mymodel_dt/m_s_</UNIT-REF>
<COMPU-INTERNAL-TO-PHYS>
<COMPU-SCALES>
<COMPU-SCALE>
<COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS>
<COMPU-NUMERATOR>
<V>-100</V>
</COMPU-NUMERATOR>
<COMPU-DENOMINATOR>
<V>0</V>
<V>-1</V>
</COMPU-DENOMINATOR>
</COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS>
</COMPU-SCALE>
</COMPU-SCALES>
</COMPU-INTERNAL-TO-PHYS>
<COMPU-PHYS-TO-INTERNAL>
<COMPU-SCALES>
<COMPU-SCALE>
<COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS>
<COMPU-NUMERATOR>
<V>100</V>
</COMPU-NUMERATOR>
<COMPU-DENOMINATOR>
<V>0</V>
<V>1</V>
</COMPU-DENOMINATOR>
</COMPU-RATIONAL-COEFFS>
</COMPU-SCALE>
</COMPU-SCALES>
</COMPU-PHYS-TO-INTERNAL>
</COMPU-METHOD>The COMPU-METHOD is referenced from the application data type generated for
T1Rec.
<APPLICATION-PRIMITIVE-DATA-TYPE UUID="...">
<SHORT-NAME>T1Rec_DualScaled</SHORT-NAME>
<CATEGORY>VALUE</CATEGORY>
<SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS>
<SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-VARIANTS>
<SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-CONDITIONAL>
<SW-CALIBRATION-ACCESS>READ-WRITE</SW-CALIBRATION-ACCESS>
<COMPU-METHOD-REF DEST="COMPU-METHOD">/mymodel_pkg/mymodel_dt/CM3</COMPU-METHOD-REF>
<DATA-CONSTR-REF DEST="DATA-CONSTR">/mymodel_pkg/mymodel_dt/ApplDataTypes/
DataConstrs/DC_T1Rec_DualScaled</DATA-CONSTR-REF>
</SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-CONDITIONAL>
</SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-VARIANTS>
</SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS>
</APPLICATION-PRIMITIVE-DATA-TYPE>The application data type T1Rec_DualScaled is referenced from the parameter data prototype generated for T1Rec.
<PARAMETER-DATA-PROTOTYPE UUID="...">
<SHORT-NAME>T1Rec</SHORT-NAME>
<SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS>
<SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-VARIANTS>
<SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-CONDITIONAL>
<SW-CALIBRATION-ACCESS>READ-WRITE</SW-CALIBRATION-ACCESS>
<SW-IMPL-POLICY>STANDARD</SW-IMPL-POLICY>
</SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-CONDITIONAL>
</SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS-VARIANTS>
</SW-DATA-DEF-PROPS>
<TYPE-TREF DEST="APPLICATION-PRIMITIVE-DATA-TYPE">/mymodel_pkg/mymodel_dt/ApplDataTypes/
T1Rec_DualScaled</TYPE-TREF>
...
</PARAMETER-DATA-PROTOTYPE>