cdma2000 Waveform Generation
This example shows how to generate standard-compliant forward (downlink) and reverse (uplink) cdma2000® waveforms using the Communications Toolbox™.
Introduction
The Communications Toolbox can be used to generate preset or customized standard-compliant forward and reverse cdma2000 waveforms. Specifically, the following channels are supported:
Forward cdma2000:
Forward Pilot Channel (F-PICH)
Forward Auxiliary Pilot Channel (F-APICH)
Forward Transmit Diversity Pilot Channel (F-TDPICH)
Forward Auxiliary Transmit Diversity Pilot Channel (F-ATDPICH)
Forward Sync Channel (F-SYNC)
Forward Paging Channel (F-PCH)
Forward Quick Paging Channel (F-QPCH)
Forward Broadcast Control Channel (F-BCCH)
Forward Common Control Channel (F-CCCH)
Forward Dedicated Control Channel (F-DCCH)
Forward Common Power Control Channel (F-CPCCH)
Forward Fundamental Traffic Channel (F-FCH), including Power Control Subchannel
Forward Supplemental Code Channel (F-SCCH)
Forward Supplemental Channel (F-SCH)
Forward Packet Data Common Control Channel (F-PDCCH)
Forward Orthogonal Channel Noise (F-OCNS)
Reverse cdma2000:
Reverse Pilot Channel (R-PICH), including Power Control Subchannel
Reverse Access Channel (R-ACH)
Reverse Enhanced Access Channel (R-EACH)
Reverse Common Control Channel (R-CCCH)
Reverse Dedicated Control Channel (R-DCCH)
Reverse Fundamental Traffic Channel (R-FCH)
Reverse Supplemental Code Channel (R-SCCH)
Reverse Supplemental Channel (R-SCH)
The generated waveforms can be used for the following applications:
Golden reference for transmitter implementations
Receiver testing and algorithm development
Testing RF hardware and software
Interference testing
Waveform Generation Techniques
Waveforms can be generated using the
cdma2000ForwardWaveformGeneratorandcdma2000ReverseWaveformGeneratorfunctions. The input of these functions is a structure containing top-level waveform parameters as well as substructures containing channel-specific parameters. This example will illustrate how such structures can be constructed from scratch.Preset structure configurations can be created using the
cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannelsandcdma2000ReverseReferenceChannelsfunctions. Such preset configurations can represent common Test and Measurement scenarios or provide a good starting point (wizard) for customizing a waveform configuration.
Generation of Preset-driven Forward and Reverse cdma2000 Waveforms
The preset structure configurations can then be passed to the waveform generation functions. For example, the following commands generate all forward and reverse channels allowable for Radio Configuration 4:
forwardPresetConfig = cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannels('ALL-RC4'); forwardPresetWaveform = cdma2000ForwardWaveformGenerator(forwardPresetConfig); reversePresetConfig = cdma2000ReverseReferenceChannels('ALL-RC4'); reversePresetWaveform = cdma2000ReverseWaveformGenerator(reversePresetConfig);
Generation of a Forward cdma2000 Waveform Using Full Parameter List
Next, we illustrate the creation of equivalent configuration structures from scratch (for forward cdma2000). This is also useful for customizing the preset configurations.
fManualConfig.SpreadingRate = 'SR1'; % Spreading Rate 1 or 3 fManualConfig.Diversity = 'NTD'; % No Transmit Diversity (other options are 'OTD', 'STS') fManualConfig.QOF = 'QOF1'; % Quasi-orthogonal function 1, 2 or 3 fManualConfig.PNOffset = 0; % PN offset of Base station fManualConfig.LongCodeState = 0; % Initial long code state fManualConfig.PowerNormalization = 'Off'; % Power normalization: 'Off', 'NormalizeTo0dB' or 'NoiseFillTo0dB' fManualConfig.OversamplingRatio = 4; % Upsampling factor fManualConfig.FilterType = 'cdma2000Long'; % Filter coefficients: 'cdma2000Long', 'cdma2000Short', 'Custom' or 'Off' fManualConfig.InvertQ = 'Off'; % Negate the imaginary part of the waveform fManualConfig.EnableModulation = 'Off'; % Enable carrier modulation fManualConfig.ModulationFrequency = 0; % Modulation frequency (Hz) fManualConfig.NumChips = 1000; % Number of chips in the waveform fpich.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-PICH channel fpich.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fManualConfig.FPICH = fpich; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fapich.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-APICH channel fapich.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fapich.WalshCode = 10; % Unique Walsh code number fapich.WalshLength = 64; % Walsh code length fManualConfig.FAPICH = fapich; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration ftdpich.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-TDPICH channel ftdpich.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fManualConfig.FTDPICH = ftdpich; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fatdpich.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-ATDPICH channel fatdpich.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fatdpich.WalshCode = 11; % Unique Walsh code number fatdpich.WalshLength = 64; % Walsh code length fManualConfig.FATDPICH = fatdpich; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fpch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-PCH channel fpch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fpch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fpch.DataRate = 4800; % Data rate (bps) fpch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fpch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fpch.WalshCode = 1; % Unique Walsh code number fManualConfig.FPCH = fpch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fsync.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-SYNC channel fsync.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fsync.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fsync.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed}, numerical vector or 'SyncMessage' fManualConfig.FSYNC = fsync; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fbcch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-BCCH channel fbcch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fbcch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fbcch.DataRate = 4800; % Data rate (bps) fbcch.FrameLength = 160; % Frame length (ms) fbcch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fbcch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fbcch.WalshCode = 2; % Unique Walsh code number fbcch.CodingType = 'conv'; % Coding type: 'conv' or 'turbo' fManualConfig.FBCCH = fbcch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fcach.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-CACH channel fcach.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fcach.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fcach.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fcach.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fcach.WalshCode = 3; % Unique Walsh code number fcach.CodingType = 'conv'; % Coding type: 'conv' or 'turbo' fManualConfig.FCACH = fcach; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fccch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-CCCH channel fccch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fccch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fccch.DataRate = 9600; % Data rate (bps) fccch.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) fccch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fccch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fccch.WalshCode = 4; % Unique Walsh code number fccch.CodingType = 'conv'; % Coding type: 'conv' or 'turbo' fManualConfig.FCCCH = fccch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fcpcch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-CPCCH channel fcpcch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fcpcch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fcpcch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fcpcch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fcpcch.WalshCode = 5; % Unique Walsh code number fManualConfig.FCPCCH = fcpcch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fqpch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-QPCH channel fqpch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fqpch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fqpch.DataRate = 2400; % Data rate (bps) fqpch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fqpch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fqpch.WalshCode = 6; % Unique Walsh code number fManualConfig.FQPCH = fqpch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration ffch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-FCH channel ffch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) ffch.RadioConfiguration = 'RC4'; % Radio Configuration: 1-9 ffch.DataRate = 9600; % Data rate (bps) ffch.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) ffch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask ffch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding ffch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector ffch.WalshCode = 7; % Unique Walsh code number ffch.EnableQOF = 'Off'; % Enable QOF spreading ffch.PowerControlEnable = 'Off'; % Enable the Power Control Subchannel fManualConfig.FFCH = ffch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration focns.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-OCNS channel focns.Power = -30; % Relative channel power (dBW) focns.WalshCode = 12; % Unique Walsh code number focns.WalshLength = 128; % Walsh code length fManualConfig.FOCNS = focns; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fdcch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-DCCH channel fdcch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fdcch.RadioConfiguration = 'RC4'; % Radio Configuration: 1-9 fdcch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fdcch.DataRate = 9600; % Data rate (bps) fdcch.FrameLength = 5; % Frame length (ms) fdcch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fdcch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fdcch.WalshCode = 8; % Unique Walsh code number fdcch.EnableQOF = 'off'; % Enable QOF spreading fManualConfig.FDCCH = fdcch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration fsch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-SCH channel fsch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fsch.RadioConfiguration = 'RC4'; % Radio Configuration: 1-9 fsch.DataRate = 9600; % Data rate (bps) fsch.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) fsch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask fsch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fsch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector fsch.WalshCode = 9; % Unique Walsh code number fsch.EnableQOF = 'Off'; % Enable QOF spreading fsch.CodingType = 'conv'; % Coding type: 'conv' or 'turbo' fManualConfig.FSCH = fsch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration forwardManualWaveform = cdma2000ForwardWaveformGenerator(fManualConfig); % Demonstrate that the above two parameterization approaches are equivalent: if(isequal(forwardPresetConfig, fManualConfig)) disp([ 'Configuration structures generated with and without the ' ... 'cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Configuration structures generated with and without the cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.
Generation of a Reverse cdma2000 Waveform Using Full Parameter List
rManualConfig.RadioConfiguration = 'RC4'; % Radio Configuration: 1-6 rManualConfig.PowerNormalization = 'Off'; % Power normalization: 'Off', 'NormalizeTo0dB' or 'NoiseFillTo0dB' rManualConfig.OversamplingRatio = 4; % Upsampling factor rManualConfig.FilterType = 'cdma2000Long'; % Filter coefficients: 'cdma2000Long', 'cdma2000Short', 'Custom' or 'Off' rManualConfig.InvertQ = 'Off'; % Negate the imaginary part of the waveform rManualConfig.EnableModulation = 'Off'; % Enable carrier modulation rManualConfig.ModulationFrequency = 0; % Modulation frequency (Hz) rManualConfig.NumChips = 1000; % Number of chips in the waveform rfch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the R-FCH channel rfch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) rfch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask rfch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding rfch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector rfch.DataRate = 14400; % Data rate (bps) rfch.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) rfch.WalshCode = 1; % Unique Walsh code number rManualConfig.RFCH = rfch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration rpich.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the R-PICH channel rpich.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) rpich.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask rpich.PowerControlEnable = 'Off'; % Enable the Power Control Subchannel rManualConfig.RPICH = rpich; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration reach.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the R-EACH channel reach.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) reach.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask reach.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding reach.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector reach.DataRate = 9600; % Data rate (bps) reach.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) reach.WalshCode = 2; % Unique Walsh code number rManualConfig.REACH = reach; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration rcch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the R-CCH channel rcch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) rcch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask rcch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding rcch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector rcch.DataRate = 9600; % Data rate (bps) rcch.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) rcch.WalshCode = 3; % Unique Walsh code number rManualConfig.RCCCH = rcch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration rdcch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the R-DCCH channel rdcch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) rdcch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask rdcch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding rdcch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector rdcch.DataRate = 14400; % Data rate (bps) rdcch.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) rdcch.WalshCode = 4; % Unique Walsh code number rManualConfig.RDCCH = rdcch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration rsch1.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the R-SCH1 channel rsch1.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) rsch1.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask rsch1.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding rsch1.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector rsch1.DataRate = 14400; % Data rate (bps) rsch1.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) rsch1.WalshLength = 8; % Walsh code length rsch1.WalshCode = 5; % Unique Walsh code number rManualConfig.RSCH1 = rsch1; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration rsch2 = rsch1; % Apply the same settings with R-SCH1 rsch2.WalshCode = 6; % Except for the unique Walsh code number rManualConfig.RSCH2 = rsch2; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration reverseManualWaveform = cdma2000ReverseWaveformGenerator(rManualConfig); % Demonstrate that the above two parameterization approaches are equivalent: if(isequal(reversePresetConfig, rManualConfig)) disp([ 'Configuration structures generated with and without the ' ... 'cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Configuration structures generated with and without the cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.
Waveform Comparison
Compare the waveforms generated using both approaches described above and see that the generated waveforms are identical
if(isequal(forwardPresetWaveform, forwardManualWaveform)) disp([ 'Forward waveforms generated with and without the ' ... 'cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Forward waveforms generated with and without the cdma2000ForwardReferenceChannels function are the same.
if(isequal(reversePresetWaveform, reverseManualWaveform)) disp([ 'Reverse waveforms generated with and without the ' ... 'cdma2000ReverseReferenceChannels function are the same.']); end
Reverse waveforms generated with and without the cdma2000ReverseReferenceChannels function are the same.
Customization of Configuration
The configuration structures can be customized in order to create a waveform that better suits your objective. You can also customize the preset waveforms in order to exploit additional capabilities, such as:
% 1. Specifying the message of the Sync channel: fManualConfig2 = fManualConfig; fsync.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-SYNC channel fsync.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) fsync.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding fsync.DataSource = 'SyncMessage'; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed}, numerical vector or 'SyncMessage' sm.P_REV = 6; % Protocol Revision field sm.MIN_P_REV = 6; % Minimum Protocol Revision field sm.SID = hex2dec('14B'); % System Identifier field sm.NID = 1; % Network Identification field sm.PILOT_PN = 0; % Pilot PN Offset field sm.LC_STATE = hex2dec('20000000000'); % Long Code State field sm.SYS_TIME = hex2dec('36AE0924C'); % System Time field sm.LP_SEC = 0; % Leap Second field sm.LTM_OFF = 0; % Local Time Offset field sm.DAYLT = 0; % Daylight Savings Time Indicator field sm.PRAT = 0; % Paging Channel Data Rate field sm.CDMA_FREQ = hex2dec('2F6'); % CDMA Frequency field sm.EXT_CDMA_FREQ = hex2dec('2F6'); % Extended CDMA Frequency field fsync.SyncMessage = sm; % Sync channel message substructure, used if 'SyncMessage' is the data source fManualConfig2.FSYNC = fsync; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration % 2. Enabling the Power Control Subchannel of the Forward Fundamental Channel: ffch.Enable = 'On'; % Enable the F-FCH channel ffch.Power = 0; % Relative channel power (dBW) ffch.RadioConfiguration = 'RC4'; % Radio Configuration: 1-9 ffch.DataRate = 9600; % Data rate (bps) ffch.FrameLength = 20; % Frame length (ms) ffch.LongCodeMask = 0; % Long code mask ffch.EnableCoding = 'On'; % Enable channel coding ffch.DataSource = {'PN9', 1}; % Input message: {'PNX', Seed} or numerical vector ffch.WalshCode = 7; % Unique Walsh code number ffch.EnableQOF = 'Off'; % Enable QOF spreading ffch.PowerControlEnable = 'On'; % Enable the Power Control Subchannel ffch.PowerControlPower = 0; % Power control subchannel power (relative to F-FCH) ffch.PowerControlDataSource = {'PN9',1}; % Power control subchannel data source fManualConfig2.FFCH = ffch; % Add the channel to the waveform configuration forwardManualWaveform2 = cdma2000ForwardWaveformGenerator(fManualConfig2);
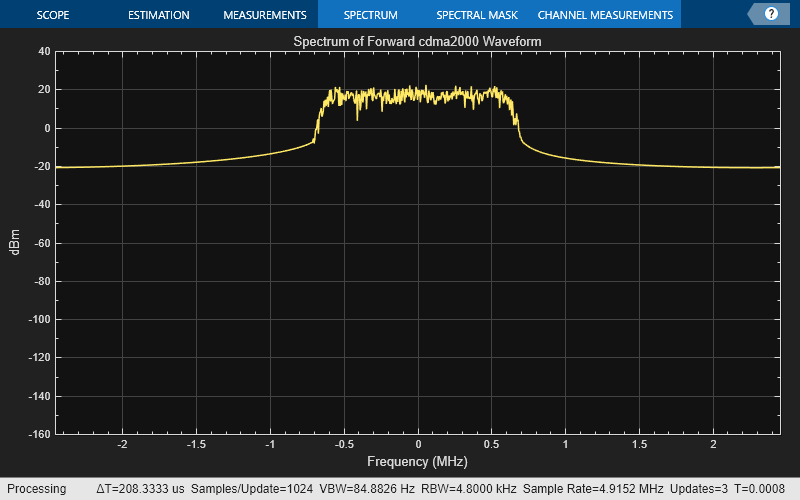
Plot Spectrum of Forward cdma2000 Waveform
Plot the spectrum of the time domain signal forwardManualWaveform.
chiprate = 1.2288e6; % Chip rate of the baseband waveform (SR1) fSpectrumPlot = spectrumAnalyzer('SampleRate', chiprate*fManualConfig.OversamplingRatio); fSpectrumPlot.Title = 'Spectrum of Forward cdma2000 Waveform'; fSpectrumPlot.YLimits = [-160,40]; fSpectrumPlot(forwardManualWaveform);
Plot Spectrum of Reverse cdma2000 Waveform
Plot the spectrum of the time domain signal reverseManualWaveform.
chiprate = 1.2288e6; % Chip rate of the baseband waveform (SR1) rSpectrumPlot = spectrumAnalyzer('SampleRate', chiprate*rManualConfig.OversamplingRatio); rSpectrumPlot.Title = 'Spectrum of Reverse cdma2000 Waveform'; rSpectrumPlot.YLimits = [-160,40]; rSpectrumPlot(reverseManualWaveform);

Selected Bibliography
C.S0002-F v2.0: Physical Layer Standard for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems.