Generate Optimized Code for Math Functions Using ARM Cortex-A CMSIS CRL
This example shows how to use the ARM Cortex-A CMSIS code replacement library (CRL) to generate optimized code for math functions on ARM® Cortex-A® hardware targets. The example walks you through the process of code generation, deployment of the generated code on the ARM Cortex-A hardware targets, and the process of measuring the performance gain achieved by using ARM Cortex-A CMSIS CRL on the selected ARM Cortex-A hardware target.
Select Math Function, Data Type and Hardware
You select the math function, data type, and hardware from the drop-down list. Create a coder.hardware object for the selected hardware. To deploy code on Raspberry Pi™, replace raspiname with the name of your Raspberry Pi, pi with your username, password with your password, and remoteBuildDir with the folder name of your choice. You generate the code inside this folder that is located in the user home directory of your Raspberry Pi.
mathFunctionName ='hAbs'; dataType =
'half'; hwname =
'Raspberry Pi (64bit)'; switch(hwname) case 'Raspberry Pi (64bit)' hw = coder.hardware(hwname); hw.DeviceAddress = 'raspiname'; hw.Username = 'pi'; hw.Password = 'password'; hw.BuildDir = '~/remoteBuildDir'; case 'Raspberry Pi' hw = coder.hardware(hwname); hw.DeviceAddress = 'raspiname'; hw.Username = 'pi'; hw.Password = 'password'; hw.BuildDir = '~/remoteBuildDir'; case 'ARM Cortex-A9 (QEMU)' hw = coder.hardware(hwname); otherwise hw = coder.hardware('ARM Cortex-A9 (QEMU)'); end
Create Embedded Coder Configuration and Generate Code
Create a coder.config object for a static library and set the verification mode to PIL.
cfg = coder.config('lib','ecoder',true); cfg.VerificationMode = 'PIL';
Set the hardware property of the coder.config object cfg to the coder.hardware object hw and display the automatically selected toolchain.
cfg.Hardware = hw; disp(cfg.Toolchain)
GNU GCC Embedded Linux
You set the CodeReplacementLibrary to ARM Cortex-A CMSIS and print the Toolchain that is set automatically sets when you select the Raspberry Pi Hardware.
cfg.CodeReplacementLibrary = 'ARM Cortex-A CMSIS';Create an input vector of desired length and convert the input to the selected data type.
vectorLength = 1000; input = feval(dataType,rand([vectorLength,1]));
Use the codegen function to generate code for the selected math function.
codegen('-config', cfg, '-args', '{input}', mathFunctionName, '-launchreport')
### Connectivity configuration for function 'hAbs': 'Raspberry Pi' Location of the generated elf : /home/pi/remoteBuildDirExample/MATLAB_ws/R2024a/V/24a/Example/codegen/lib/hAbs/pil Code generation successful: View report
Verify CMSIS Code Replacement in Code Generation Report
The codegen command, when you use it with the launchreport option in the command line, opens a code generation report as shown below. Click Trace Code to examine the generated CMSIS call and its mapping to the corresponding MATLAB Code. The generated macro mw_arm_abs_f16 is defined by the generated file mw_cmsis_f16.h defines. This macro calls the optimized CMSIS-DSP library function arm_abs_f16.
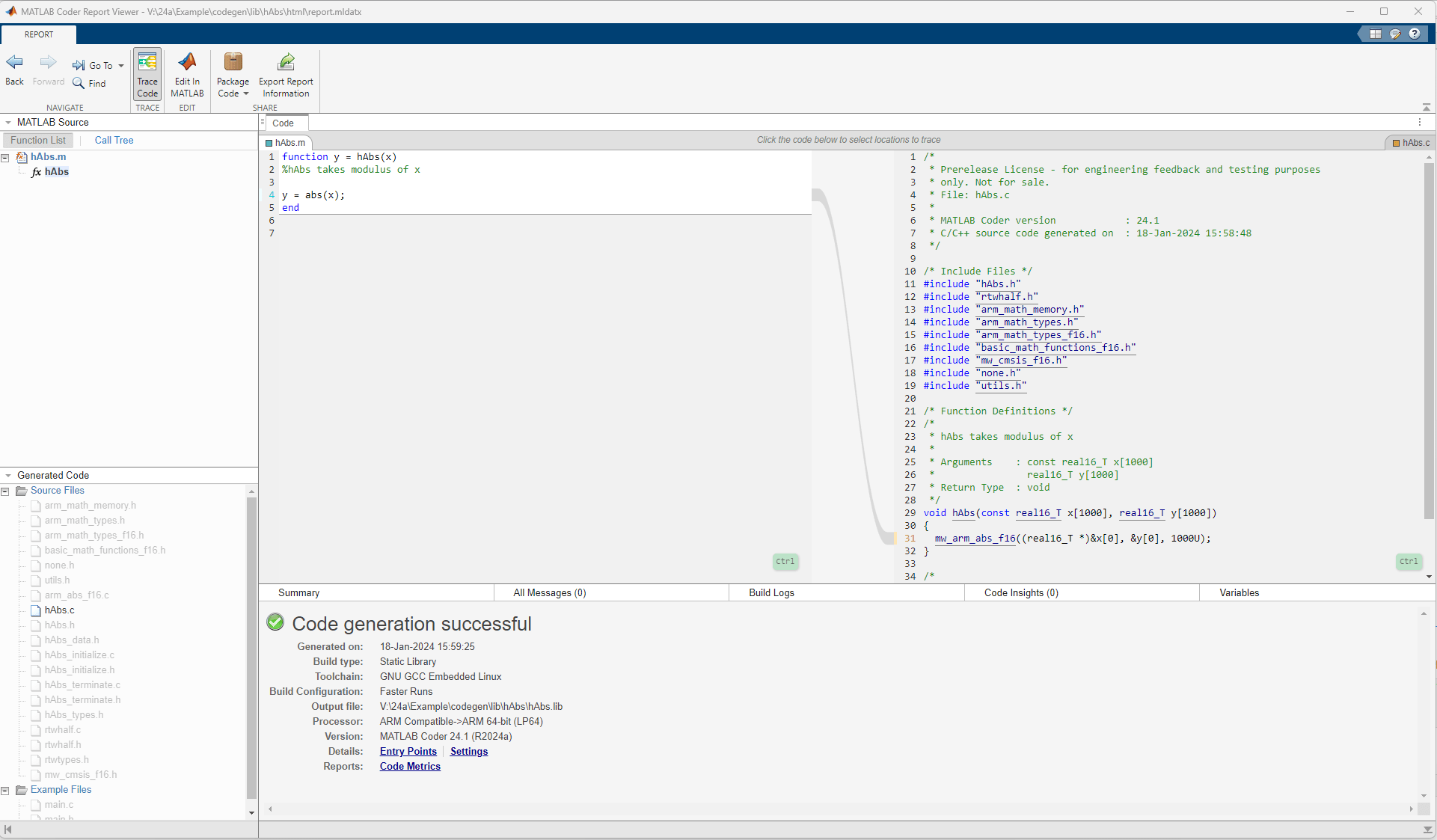
Run PIL Simulation and Verify Accuracy
Use the feval function to compute the output ref of the MATLAB function. You compute the output dut of the CMSIS code by calling the generated processor-in-the-loop (PIL) function that runs on the hardware target. To verify accuracy, compute the root mean squared error between the expected MATLAB output ref and the processor-in-the-loop (PIL) output dut.
ref = feval(mathFunctionName,input);
pilFunctionName = [mathFunctionName,'_pil'];
dut = feval(pilFunctionName,input);### Starting application: 'codegen\lib\hAbs\pil\hAbs.elf'
To terminate execution: clear hAbs_pil
### Launching application hAbs.elf...
rmsError = sqrt(sum((ref - dut).^2) ./ vectorLength)
rmsError =
half
0
Use sprintf to form the command to clear the PIL function.
ClearPilCommand = sprintf('clear %s',pilFunctionName);Terminate the PIL execution.
eval(ClearPilCommand)
### Host application produced the following standard output (stdout) and standard error (stderr) messages:
Measure Performance Gain
You calculate the ratio of the execution time of the code generated with and without ARM Cortex-A CMSIS CRL.
Measure Execution Time of CMSIS-DSP Code
Use processor-in-the-loop (PIL) workflow to measure the execution time of the code running on the target hardware or the hardware emulator. Generate a PIL function after setting the CodeExecutionProfiling field of the codegen configuration to true.
cfg.CodeExecutionProfiling = true; cfg.CodeReplacementLibrary = 'ARM Cortex-A CMSIS'; codegen('-config', cfg, '-args', '{input}', mathFunctionName)
### Connectivity configuration for function 'hAbs': 'Raspberry Pi' Location of the generated elf : /home/pi/remoteBuildDirExample/MATLAB_ws/R2024a/V/24a/Example/codegen/lib/hAbs/pil Code generation successful.
Call the generated PIL function 1000 times to get the average execution time.
numCalls = 1000; for k = 1:numCalls input = feval(dataType,rand([vectorLength,1])); yOutCRL = feval(pilFunctionName,input); end
### Starting application: 'codegen\lib\hAbs\pil\hAbs.elf'
To terminate execution: clear hAbs_pil
### Launching application hAbs.elf...
Execution profiling data is available for viewing. Open Simulation Data Inspector.
Execution profiling report will be available after termination.
Terminate the PIL execution.
eval(ClearPilCommand)
### Host application produced the following standard output (stdout) and standard error (stderr) messages:
Execution profiling report: coder.profile.show(getCoderExecutionProfile('hAbs'))
Generate an execution profile report to evaluate the execution time.
executionProfileCMSIS = getCoderExecutionProfile(mathFunctionName); report(executionProfileCMSIS, ... 'Units','Seconds', ... 'ScaleFactor','1e-03', ... 'NumericFormat','%0.4f')
ans = 'V:\24a\Example\codegen\lib\hAbs\html\orphaned\ExecutionProfiling_3af97336ef70a4c0.html'
executionTimeCMSIS = mean([executionProfileCMSIS.Sections.ExecutionTimeInSeconds]);
Measure Execution Time of Plain C Code
cfg.CodeReplacementLibrary = 'none'; codegen('-config', cfg, '-args', '{input}', mathFunctionName)
### Connectivity configuration for function 'hAbs': 'Raspberry Pi' Location of the generated elf : /home/pi/remoteBuildDirExample/MATLAB_ws/R2024a/V/24a/Example/codegen/lib/hAbs/pil Code generation successful.
for k = 1:numCalls input = feval(dataType,rand([vectorLength,1]) - 0.5); yOutPlainC = feval(pilFunctionName,input); end
### Starting application: 'codegen\lib\hAbs\pil\hAbs.elf'
To terminate execution: clear hAbs_pil
### Launching application hAbs.elf...
Execution profiling data is available for viewing. Open Simulation Data Inspector.
Execution profiling report will be available after termination.
eval(ClearPilCommand)
### Host application produced the following standard output (stdout) and standard error (stderr) messages:
Execution profiling report: coder.profile.show(getCoderExecutionProfile('hAbs'))
Generate an execution profile report to evaluate execution time.
executionProfilePlainC = getCoderExecutionProfile(mathFunctionName); report(executionProfilePlainC, ... 'Units','Seconds', ... 'ScaleFactor','1e-03', ... 'NumericFormat','%0.4f')
ans = 'V:\24a\Example\codegen\lib\hAbs\html\orphaned\ExecutionProfiling_cb716401ade96c4f.html'
executionTimePlainC = mean([executionProfilePlainC.Sections.ExecutionTimeInSeconds]);
Performance Gain
Using the ARM Cortex-A CMSIS CRL for half-float inputs for the real vector absolute function achieves an impeccable performance gain of more than 8x compared to code generated without using CRL.
CMSISPerformanceGainOverPlainC = executionTimePlainC ./ executionTimeCMSIS
CMSISPerformanceGainOverPlainC = 8.5097