Three-Parameter Weibull Distribution
Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™ uses a two-parameter Weibull Distribution with a scale parameter and a shape parameter in the probability distribution object WeibullDistribution and distribution-specific functions such as wblpdf and wblcdf. The Weibull distribution can take a third parameter. The three-parameter Weibull distribution adds a location parameter that is zero in the two-parameter case. If has a two-parameter Weibull distribution, then has a three-parameter Weibull distribution with the added location parameter .
The probability density function (pdf) of the three-parameter Weibull distribution becomes
where and are positive values, and is a real value.
If the scale parameter is less than 1, the probability density of the Weibull distribution approaches infinity as approaches . The maximum of the likelihood function is infinite. The software might find satisfactory estimates in some cases, but the global maximum is degenerate when .
This example shows how to find the maximum likelihood estimates (MLEs) for the three-parameter Weibull distribution by using a custom defined pdf and the mle function. Also, the example explains how to avoid the problem of a pdf approaching infinity when .
Load Data
Load the carsmall data set, which contains measurements of cars made in the 1970s and early 1980s.
load carsmallThis example uses car weight measurements in the Weight variable.
Fit Two-Parameter Weibull Distribution
First, fit a two-parameter Weibull distribution to Weight.
pd = fitdist(Weight,'Weibull')pd =
WeibullDistribution
Weibull distribution
A = 3321.64 [3157.65, 3494.15]
B = 4.10083 [3.52497, 4.77076]
Plot the fit with a histogram.
figure histogram(Weight,8,'Normalization','pdf') hold on x = linspace(0,6000); plot(x,pdf(pd,x),'LineWidth',2) hold off
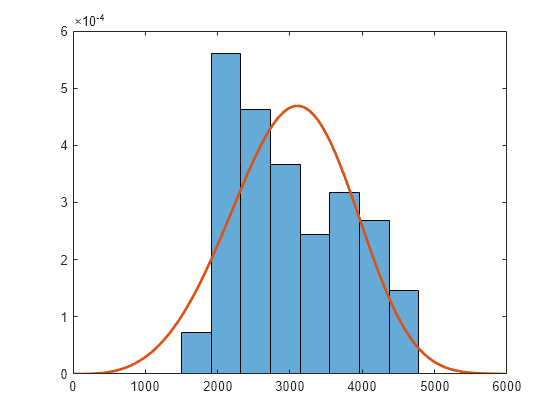
The fitted distribution plot does not match the histogram well. The histogram shows no samples in the region where Weight < 1500. Fit a Weibull distribution again after subtracting 1500 from Weight.
pd = fitdist(Weight-1500,'Weibull')pd =
WeibullDistribution
Weibull distribution
A = 1711.75 [1543.58, 1898.23]
B = 1.99963 [1.70954, 2.33895]
figure histogram(Weight-1500,8,'Normalization','pdf') hold on plot(x,pdf(pd,x),'LineWidth',2) hold off

The fitted distribution plot matches the histogram better.
Instead of specifying an arbitrary value for the distribution limit, you can define a custom function for a three-parameter Weibull distribution and estimate the limit (location parameter ).
Define Custom pdf for Three-Parameter Weibull Distribution
Define a probability density function for a three-parameter Weibull distribution.
f_def = @(x,a,b,c) (x>c).*(b/a).*(((x-c)/a).^(b-1)).*exp(-((x-c)/a).^b);
Alternatively, you can use the wblpdf function to define the three-parameter Weibull distribution.
f = @(x,a,b,c) wblpdf(x-c,a,b);
Fit Three-Parameter Weibull Distribution
Find the MLEs for the three parameters by using the mle function. You must also specify the initial parameter values (Start name-value argument) for the custom distribution.
try mle(Weight,'pdf',f,'Start',[1700 2 1500]) catch ME disp(ME) end
MException with properties:
identifier: 'stats:mle:NonpositivePdfVal'
message: 'Custom probability function returned negative or zero values.'
cause: {}
stack: [13×1 struct]
Correction: []
mle returns an error because the custom function returns nonpositive values. This error is a typical problem when you fit a lower limit of a distribution, or fit a distribution with a region that has zero probability density. mle tries some parameter values that have zero density, and then fails to estimate parameters. In the previous function call, mle tries values of that are higher than the minimum value of Weight, which leads to a zero density for some points, and returns the error.
To avoid this problem, you can turn off the option that checks for invalid function values and specify the parameter bounds when you call the mle function.
Display the default options for the iterative estimation process of the mle function.
statset('mlecustom')ans = struct with fields:
Display: 'off'
MaxFunEvals: 400
MaxIter: 200
TolBnd: 1.0000e-06
TolFun: 1.0000e-06
TolTypeFun: []
TolX: 1.0000e-06
TolTypeX: []
GradObj: 'off'
Jacobian: []
DerivStep: 6.0555e-06
FunValCheck: 'on'
Robust: []
RobustWgtFun: []
WgtFun: []
Tune: []
UseParallel: []
UseSubstreams: []
Streams: {}
OutputFcn: []
Override that default, using an options structure created with the statset function. Specify the FunValCheck field value as 'off' to turn off the validity check for the custom function values.
opt = statset('FunValCheck','off');
Find the MLEs of the three parameters again. Specify the iterative process option (Options name-value argument) and parameter bounds (LowerBound and UpperBound name-value arguments). The scale and shape parameters must be positive, and the location parameter must be smaller than the minimum of the sample data.
params = mle(Weight,'pdf',f,'Start',[1700 2 1500],'Options',opt, ... 'LowerBound',[0 0 -Inf],'UpperBound',[Inf Inf min(Weight)])
params = 1×3
103 ×
1.3874 0.0015 1.7581
Plot the fit with a histogram.
figure histogram(Weight,8,'Normalization','pdf') hold on plot(x,f(x,params(1),params(2),params(3)),'LineWidth',2) hold off

The fitted distribution plot matches the histogram well.
Fit Three-Parameter Weibull Distribution for
If the scale parameter is less than 1, the pdf of the Weibull distribution approaches infinity near the lower limit (location parameter). You can avoid this problem by specifying interval-censored data, if appropriate.
Load the cities data set. The data includes ratings for nine different indicators of the quality of life in 329 US cities: climate, housing, health, crime, transportation, education, arts, recreation, and economics. For each indicator, a higher rating is better.
load citiesFind the MLEs for the seventh indicator (arts).
Y = ratings(:,7); params1 = mle(Y,'pdf',f,'Start',[median(Y) 1 0],'Options',opt)
Warning: Maximum likelihood estimation did not converge. Iteration limit exceeded.
params1 = 1×3
103 ×
2.7584 0.0008 0.0520
The warning message indicates that the estimation does not converge. Modify the estimation options, and find the MLEs again. Increase the maximum number of iterations (MaxIter) and the maximum number of objective function evaluations (MaxFunEvals).
opt.MaxIter = 1e3; opt.MaxFunEvals = 1e3; params2 = mle(Y,'pdf',f,'Start',params1,'Options',opt)
Warning: Maximum likelihood estimation did not converge. Function evaluation limit exceeded.
params2 = 1×3
103 ×
2.7407 0.0008 0.0520
The iteration still does not converge because the pdf approaches infinity near the lower limit.
Assume that the indicators in Y are the values rounded to the nearest integer. Then, you can treat values in Y as interval-censored observations. An observation y in Y indicates that the actual rating is between y–0.5 and y+0.5. Create a matrix in which each row represents the interval surrounding each integer in Y.
intervalY = [Y-0.5, Y+0.5];
Find the MLEs again using intervalY. To fit a custom distribution to a censored data set, you must pass both the pdf and cdf to the mle function.
F = @(x,a,b,c) wblcdf(x-c,a,b); params = mle(intervalY,'pdf',f,'cdf',F,'Start',params2,'Options',opt)
params = 1×3
103 ×
2.7949 0.0008 0.0515
The function finds the MLEs without any convergence issues. This fit is based on fitting probabilities to intervals, so it does not encounter the problem of a density approaching infinity at a single point. You can use this approach only when converting data to an interval-censored version is appropriate.
Plot the results.
figure histogram(Y,'Normalization','pdf') hold on x = linspace(0,max(Y)); plot(x,f(x,params(1),params(2),params(3)),'LineWidth',2) hold off
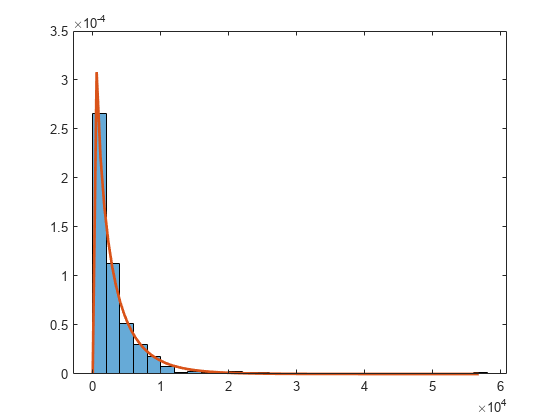
The fitted distribution plot matches the histogram well.
See Also
WeibullDistribution | mle | wblcdf | wblpdf