gammaln
Logarithmic gamma function
Syntax
Description
Examples
Logarithmic Gamma Function for Numeric and Symbolic Arguments
Depending on its arguments, gammaln returns
floating-point or exact symbolic results.
Compute the logarithmic gamma function for these numbers. Because these numbers are not symbolic objects, you get floating-point results.
A = gammaln([1/5, 1/2, 2/3, 8/7, 3])
A =
1.5241 0.5724 0.3032 -0.0667 0.6931Compute the logarithmic gamma function for the numbers converted
to symbolic objects. For many symbolic (exact) numbers, gammaln returns
results in terms of the gammaln, log,
and gamma functions.
symA = gammaln(sym([1/5, 1/2, 2/3, 8/7, 3]))
symA = [ gammaln(1/5), log(pi^(1/2)), gammaln(2/3),... log(gamma(1/7)/7), log(2)]
Use vpa to approximate symbolic results
with floating-point numbers:
vpa(symA)
ans = [ 1.5240638224307845248810564939263,... 0.57236494292470008707171367567653,... 0.30315027514752356867586281737201,... -0.066740877459477468649396334098109,... 0.69314718055994530941723212145818]
Definition of the Logarithmic Gamma Function on Complex Plane
gammaln is defined for
all complex arguments, except negative infinity.
Compute the logarithmic gamma function for positive integer
arguments. For such arguments, the logarithmic gamma function is defined
as the natural logarithm of the gamma function, gammaln(x)
= log(gamma(x)).
pos = gammaln(sym([1/4, 1/3, 1, 5, Inf]))
pos = [ log((pi*2^(1/2))/gamma(3/4)), log((2*pi*3^(1/2))/(3*gamma(2/3))), 0, log(24), Inf]
Compute the logarithmic gamma function for nonpositive integer
arguments. For nonpositive integers, gammaln returns Inf.
nonposint = gammaln(sym([0, -1, -2, -5, -10]))
nonposint = [ Inf, Inf, Inf, Inf, Inf]
Compute the logarithmic gamma function for complex and negative
rational arguments. For these arguments, gammaln returns
unresolved symbolic calls.
complex = gammaln(sym([i, -1 + 2*i , -2/3, -10/3]))
complex = [ gammaln(1i), gammaln(- 1 + 2i), gammaln(-2/3), gammaln(-10/3)]
Use vpa to approximate symbolic results
with floating-point numbers:
vpa(complex)
ans = [ - 0.65092319930185633888521683150395 - 1.8724366472624298171188533494366i,... - 3.3739449232079248379476073664725 - 3.4755939462808110432931921583558i,... 1.3908857550359314511651871524423 - 3.1415926535897932384626433832795i,... - 0.93719017334928727370096467598178 - 12.566370614359172953850573533118i]
Compute the logarithmic gamma function of negative infinity:
gammaln(sym(-Inf))
ans = NaN
Plot Logarithmic Gamma Function
Plot the logarithmic gamma function on the interval from 0 to 10.
syms x fplot(gammaln(x),[0 10]) grid on
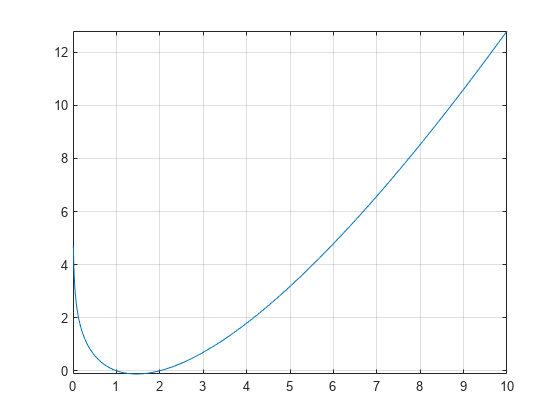
To see the negative values better, plot the same function on the interval from 1 to 2.
fplot(gammaln(x),[1 2])
grid on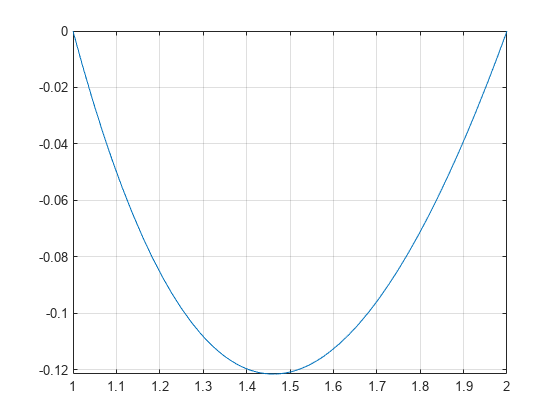
Handle Expressions Containing Logarithmic Gamma Function
Many functions, such as diff and limit,
can handle expressions containing lngamma.
Differentiate the logarithmic gamma function:
syms x diff(gammaln(x), x)
ans = psi(x)
Compute the limits of these expressions containing the logarithmic gamma function:
syms x limit(1/gammaln(x), x, Inf)
ans = 0
limit(gammaln(x - 1) - gammaln(x - 2), x, 0)
ans = log(2) + pi*1i
Input Arguments
Algorithms
For single or double input to gammaln(x), x must
be real and positive.
For symbolic input,
gammaln(x)is defined for all complexxexcept the singular points 0, -1, -2, ... .For positive real
x,gammaln(x)represents the logarithmic gamma functionlog(gamma(x)).For negative real
xor for complexx, gammaln(x) = log(gamma(x)) + f(x)2πi where f(x) is some integer valued function. The integer multiples of 2πi are chosen such thatgammaln(x)is analytic throughout the complex plane with a branch cut along the negative real semi axis.For negative real
x,gammaln(x)is equal to the limit oflog(gamma(x))from ‘above’.
Version History
Introduced in R2014a
