phased.PhaseShiftBeamformer
Narrowband phase shift beamformer
Description
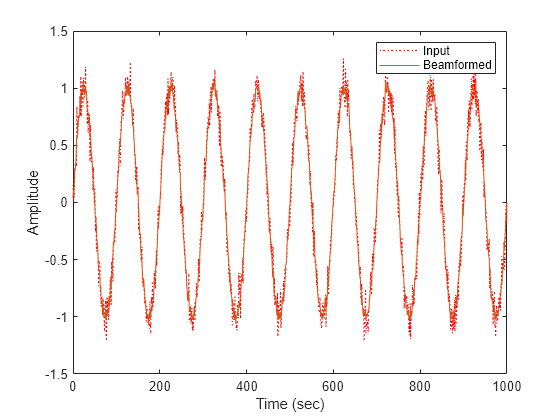
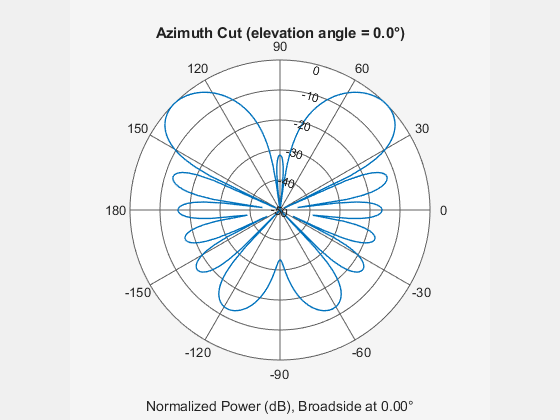
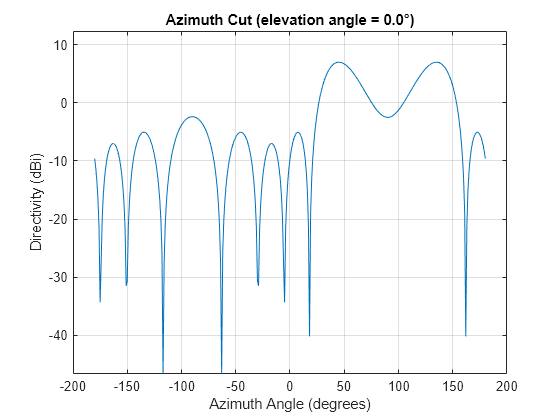
The phased.PhaseShiftBeamformer object implements a narrowband phase-shift beamformer. A phase-shift beamformer approximates a time-delay beamformer for narrowband signals by phase-shifting the arriving signal. A phase shift beamformer belongs to the family of conventional beamformers.
To beamform signals arriving at an array:
Create the
phased.PhaseShiftBeamformerobject and set its properties.Call the object with arguments, as if it were a function.
To learn more about how System objects work, see What Are System Objects?
Creation
Description
beamformer = phased.PhaseShiftBeamformerbeamformer, with default property values.
beamformer = phased.PhaseShiftBeamformer(Name,Value)Name set to a
specified Value. You can specify additional name-value pair arguments
in any order as
(Name1,Value1,...,NameN,ValueN).
Enclose each property name in single quotes.
Example: beamformer =
phased.PhaseShiftBeamformer('SensorArray',phased.URA,'OperatingFrequency',300e6)
sets the sensor array to a uniform rectangular array (URA) with default URA property
values. The beamformer has an operating frequency of 300 MHz.
Properties
Usage
Description
Y = beamformer(X)X, and returns
the beamformed output in Y. To use this syntax, set DirectionSource to 'Property' and set the beamforming
direction using the Direction property.
Y = beamformer(X,ANG)ANG input argument to set the beamforming direction. To use
this syntax, set the DirectionSource property to 'Input port'.
[
returns the beamforming weights, Y,W] =
beamformer(___)W. To use this syntax, set the
WeightsOutputPort property to true.
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Object Functions
To use an object function, specify the
System object as the first input argument. For
example, to release system resources of a System object named obj, use
this syntax:
release(obj)
Examples
Algorithms
References
[1] Van Trees, H.L. Optimum Array Processing. New York, NY: Wiley-Interscience, 2002.
[2] Johnson, Don H. and D. Dudgeon. Array Signal Processing. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1993.
[3] Van Veen, B.D. and K. M. Buckley. “Beamforming: A versatile approach to spatial filtering”. IEEE ASSP Magazine, Vol. 5 No. 2 pp. 4–24.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2011a