lambertw
Lambert W function
Syntax
Description
Examples
The Lambert W function W(x) is a set of
solutions of the equation x =
W(x)eW(x).
Solve this equation. The solution is the Lambert W function.
syms x W eqn = x == W*exp(W); solve(eqn,W)
ans = lambertw(0, x)
Verify that branches of the Lambert W function are valid solutions of the
equation x = W*eW:
k = -2:2; eqn = subs(eqn,W,lambertw(k,x)); isAlways(eqn)
ans =
1×5 logical array
1 1 1 1 1Depending on its arguments, lambertw can
return floating-point or exact symbolic results.
Compute the Lambert W functions for these numbers. Because the numbers are not symbolic objects, you get floating-point results.
A = [0 -1/exp(1); pi i]; lambertw(A)
ans = 0.0000 + 0.0000i -1.0000 + 0.0000i 1.0737 + 0.0000i 0.3747 + 0.5764i
lambertw(-1,A)
ans =
-Inf + 0.0000i -1.0000 + 0.0000i
-0.3910 - 4.6281i -1.0896 - 2.7664iCompute the Lambert W functions for the numbers converted to symbolic objects.
For most symbolic (exact) numbers, lambertw returns unresolved
symbolic calls.
A = [0 -1/exp(sym(1)); pi i]; W0 = lambertw(A)
W0 = [ 0, -1] [ lambertw(0, pi), lambertw(0, 1i)]
Wmin1 = lambertw(-1,A)
Wmin1 = [ -Inf, -1] [ lambertw(-1, pi), lambertw(-1, 1i)]
Convert symbolic results to double by using double.
double(W0)
ans = 0.0000 + 0.0000i -1.0000 + 0.0000i 1.0737 + 0.0000i 0.3747 + 0.5764i
Plot the two main branches, and , of the Lambert W function.
syms x fplot(lambertw(x)) hold on fplot(lambertw(-1,x)) hold off axis([-0.5 4 -4 2]) title('Lambert W function, two main branches') legend('k=0','k=1','Location','best')

Plot the principal branch of the Lambert W function on the complex plane.
Plot the real value of the Lambert W function by using fmesh. Simultaneously plot the contours by setting 'ShowContours' to 'On'.
syms x y f = lambertw(x + 1i*y); interval = [-100 100 -100 100]; fmesh(real(f),interval,'ShowContours','On')

Plot the imaginary value of the Lambert W function. The plot has a branch cut along the negative real axis. Plot the contours separately.
fmesh(imag(f),interval)

fcontour(imag(f),interval,'Fill','on')
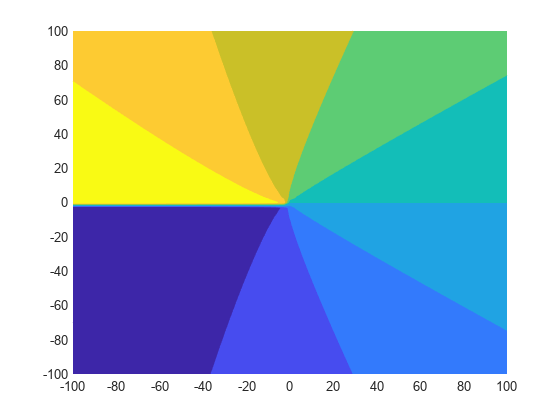
Plot the absolute value of the Lambert W function.
fmesh(abs(f),interval,'ShowContours','On')

Input Arguments
Input, specified as a number, vector, matrix, or array, or a symbolic number, variable, array, function, or expression.
At least one input argument must be a scalar, or both arguments must be vectors
or matrices of the same size. If one input argument is a scalar and the other is a
vector or matrix, lambertw expands the scalar into a vector or
matrix of the same size as the other argument with all elements equal to that
scalar.
Branch of Lambert W function, specified as an integer, a vector or matrix of integers, a symbolic integer, or a symbolic vector or matrix of integers.
At least one input argument must be a scalar, or both arguments must be vectors
or matrices of the same size. If one input argument is a scalar and the other is a
vector or matrix, lambertw expands the scalar into a vector or
matrix of the same size as the other argument with all elements equal to that
scalar.
More About
The Lambert W function W(x) represents the solutions y of the equation for any complex number x.
For complex x, the equation has an infinite number of solutions y = lambertW(k,x) where k ranges over all integers.
For all real x ≥ 0, the equation has exactly one real solution y = lambertW(x) = lambertW(0,x).
For real x where , the equation has exactly two real solutions. The larger solution is represented by y = lambertW(x) and the smaller solution by y = lambertW(–1,x).
For , the equation has exactly one real solution y = –1 = lambertW(0, –exp(–1)) = lambertW(–1, -exp(–1)).
References
[1] Corless, R.M., G.H. Gonnet, D.E.G. Hare, D.J. Jeffrey, and D.E. Knuth. "On the Lambert W Function." Advances in Computational Mathematics, Vol. 5, pp. 329–359, 1996.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)