lwtcoef2
Description
y = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh)ll and the horizontal
(lh), vertical (hl), and diagonal
(hh) wavelet coefficients. The coefficients in
ll, lh, hl, and
hh are the outputs of lwt2 using default values.
Examples
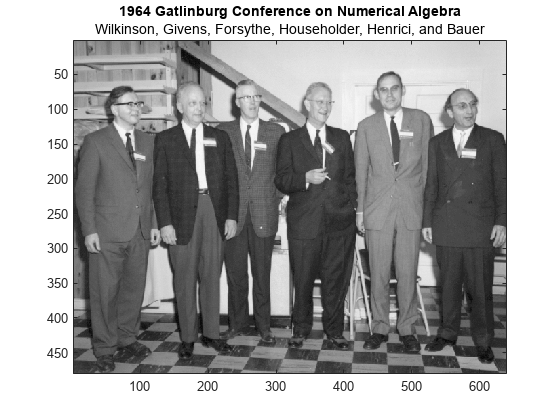
Load and plot a grayscale image.
load gatlin figure image(X) colormap(map) title("1964 Gatlinburg Conference on Numerical Algebra",... "Wilkinson, Givens, Forsythe, Householder, Henrici, and Bauer")
Create a lifting scheme associated with the bior3.7 wavelet. Use the lifting scheme to obtain the wavelet decomposition of the image to the maximum level.
lscheme = liftingScheme(Wavelet="bior3.7");
[ll,lh,hl,hh] = lwt2(X,LiftingScheme=lscheme);Extract and display the approximation coefficients at level 2. Confirm the row and column dimensions are one-quarter the size of those of the original image.
approxCF = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,... LiftingScheme=lscheme,OutputType="coefficients",Level=2); figure image(approxCF) colormap(map)
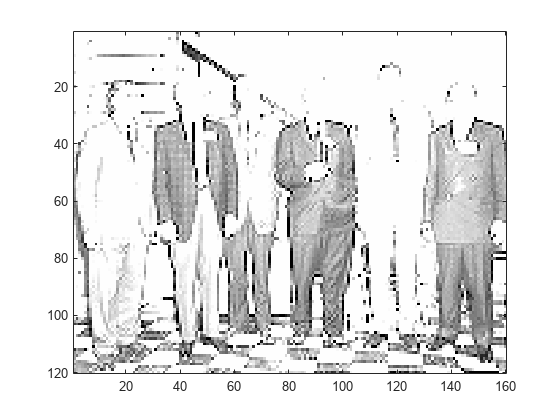
size(X)./size(approxCF)
ans = 1×2
4 4
Obtain the orthogonal projection of the level 1 approximation coefficients. Also obtain the orthogonal projections of the detail coefficients at level 1. Display the projections corresponding to the LH and HL detail coefficients. Observe that the prominent features in the LH- and HL-derived images correspond to the horizontal, and vertical features, respectively, of the original image.
approx = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,... LiftingScheme=lscheme,OutputType="projection",Level=1); dLH = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,... LiftingScheme=lscheme,OutputType="projection",Level=1,Type="LH"); dHL = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,... LiftingScheme=lscheme,OutputType="projection",Level=1,Type="HL"); dHH = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,... LiftingScheme=lscheme,OutputType="projection",Level=1,Type="HH"); subplot(1,2,1) imagesc(dLH) title("LH - Horizontal") subplot(1,2,2) imagesc(dHL) title("HL - Vertical")

Confirm the sum of the four projections equals the original image.
max(max(abs(X-(approx+dLH+dHL+dHH))))
ans = 2.3448e-13
Input Arguments
Approximation coefficients at the coarsest scale, specified as a scalar,
vector, or matrix. The coefficients are the output of lwt2.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Horizontal detail coefficients by level, specified as a
LEV-by-1 cell array, where LEV is
the level of the decomposition. The elements of lh are
in order of decreasing resolution. The coefficients are the output of
lwt2.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Vertical detail coefficients by level, specified as a
LEV-by-1 cell array, where LEV is
the level of the decomposition. The elements of hl are
in order of decreasing resolution. The coefficients are the output of
lwt2.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Diagonal detail coefficients by level, specified as a
LEV-by-1 cell array, where LEV is
the level of the decomposition. The elements of hh are
in order of decreasing resolution. The coefficients are the output of
lwt2.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: y =
lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,OutputType="projection",LiftingScheme=lscheme)
Orthogonal or biorthogonal wavelet, specified as a character vector or
string scalar. See the Wavelet property of liftingScheme for
the list of supported wavelets. The specified wavelet must match the
value that you used to obtain the coefficients ll,
lh, hl, and
hh.
You cannot specify Wavelet and
LiftingScheme at the same time.
Example: y = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,Wavelet="bior3.5")
uses the bior3.5 biorthogonal wavelet.
Data Types: char | string
Lifting scheme, specified as a liftingScheme object. The specified lifting scheme must be
the same lifting scheme that you used to obtain the coefficients
ll, lh,
hl, and hh.
You cannot specify LiftingScheme and
Wavelet at the same time.
Example: y =
lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,LiftingScheme=lScheme) uses the
lScheme lifting scheme.
Output type, specified as one of these:
"coefficients"— Extract the approximation or details coefficients"projection"— Return the projection (reconstruction) of the approximation or details coefficients
Example: y =
lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,OutputType="projection",Type="detail")
returns the projection corresponding to the detail coefficients at the
finest scale.
Type of coefficients to extract or reconstruct, specified as one of these:
"ll"— Approximation coefficients"lh"— Horizontal coefficients"hl"— Vertical coefficients"hh"— Diagonal coefficients
Example: y = lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,Type="hh")
extracts the diagonal coefficients at the finest scale.
Level of coefficients to extract or reconstruct, specified as a
positive integer less than or equal to
length(.hh)
Example: y =
lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,LiftingScheme=lsc,Level=3) uses the
lifting scheme lsc to extract the approximation
coefficients at level 3.
Data Types: double
Extension mode to use to extract or reconstruct the coefficients, specified as one of these:
"periodic"— Periodized extension"zeropad"— Zero padding"symmetric"— Symmetric extension
This argument specifies how to extend the signal at the
boundaries. The extension mode must match the value you used to generate
ll, lh,
hl, and hh.
Example: y =
lwtcoef2(ll,lh,hl,hh,Extension="zeropad") specifies zero
padding.
Output Arguments
Extracted coefficients or projection, returns as a matrix.
y has the same dimensionality as the input used by
the lwt2 function to
generate the approximation and details coefficients.
Data Types: single | double
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2021bThe lwtcoef2 input syntax has changed. Use name-value
arguments instead.
| Functionality | Result | Use Instead | Compatibility Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
Y =
lwtcoef2(TYPE,XDEC,LS,LEVEL,LEVEXT) | Errors |
| According to the value of
|
See Also
lwt2 | ilwt2 | liftingScheme
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)