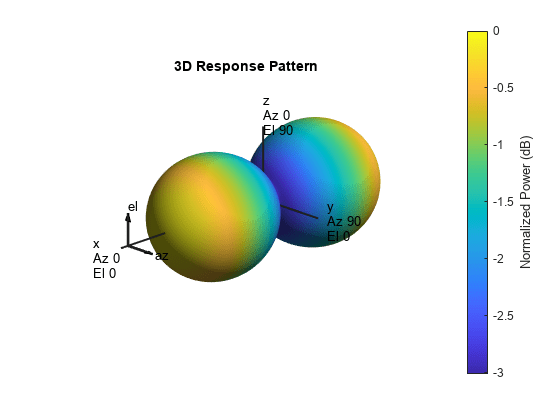phased.CrossedDipoleAntennaElement
Crossed-dipole antenna element
Description
The phased.CrossedDipoleAntennaElement
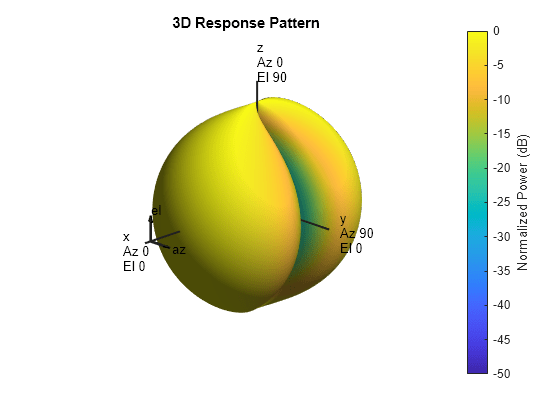
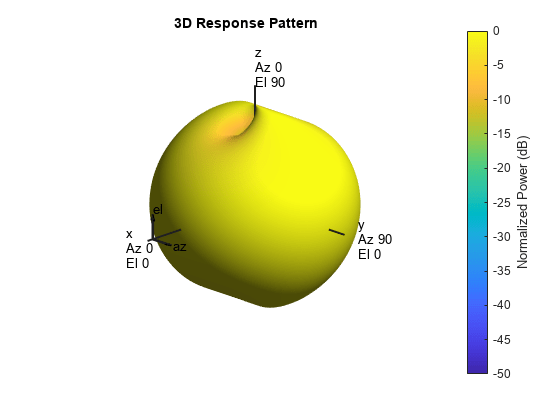
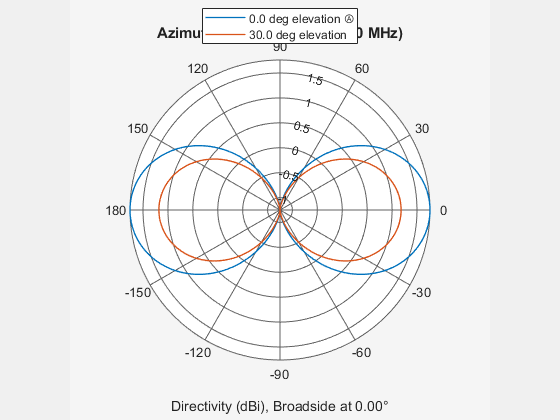
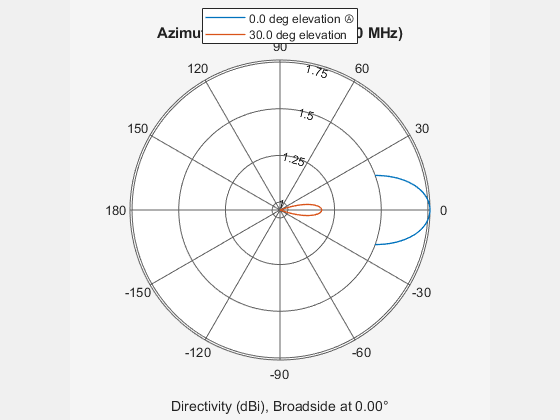
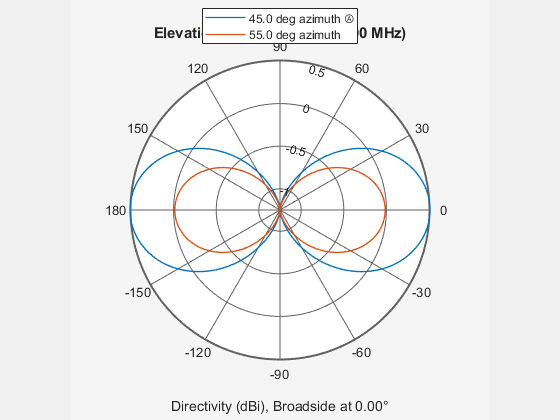
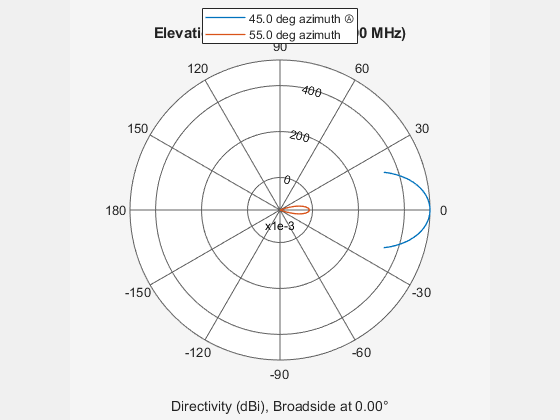
System object™ models a crossed-dipole antenna element which is used to
generate circularly polarized fields. A crossed-dipole antenna is formed from two orthogonal
short-dipole antennas. By default, one dipole lies along y-axis and the
other along the z-axis in the antenna local coordinate system. You can
rotate the antenna in the yz-plane using the
RotationAngle property. This antenna object generates right hand or
left hand circularly polarized fields, or linearly polarized fields controlled using the
Polarization property. These fields are pure along the
x-axis (defined by 0° azimuth and 0° elevation angles).
To compute the response of the antenna element:
Create the
phased.CrossedDipoleAntennaElementobject and set its properties.Call the object with arguments, as if it were a function.
To learn more about how System objects work, see What Are System Objects?
Creation
Syntax
Description
antenna = phased.CrossedDipoleAntennaElementantenna with default property values.
antenna = phased.CrossedDipoleAntennaElement(Name,Value)antenna with each specified property set to
the specified value. You can specify additional name-value pair arguments in any order as
(Name1,Value1,...,NameN,ValueN).
Properties
Usage
Syntax
Description
Note
The object performs an initialization the first time the object is executed. This
initialization locks nontunable properties
and input specifications, such as dimensions, complexity, and data type of the input data.
If you change a nontunable property or an input specification, the System object issues an error. To change nontunable properties or inputs, you must first
call the release method to unlock the object.
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Object Functions
To use an object function, specify the
System object as the first input argument. For
example, to release system resources of a System object named obj, use
this syntax:
release(obj)
Examples
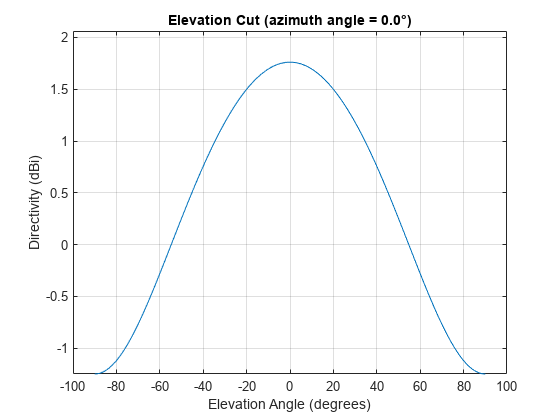
Algorithms
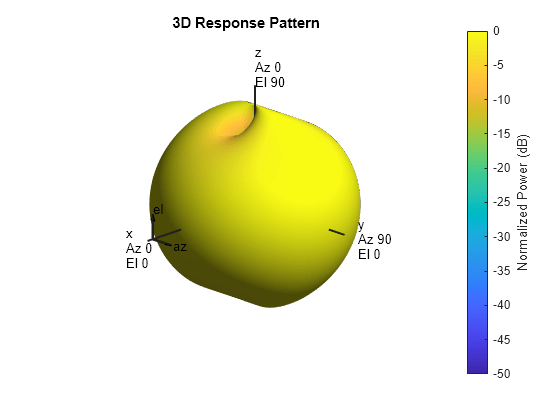
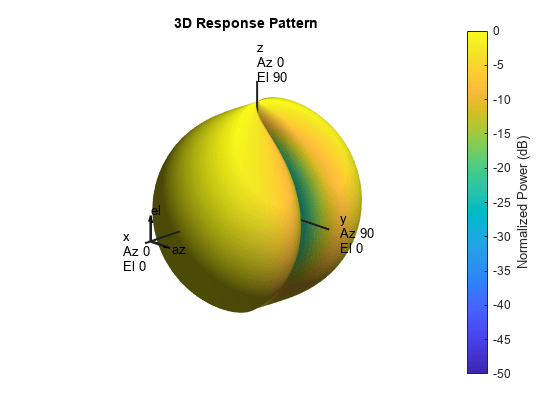
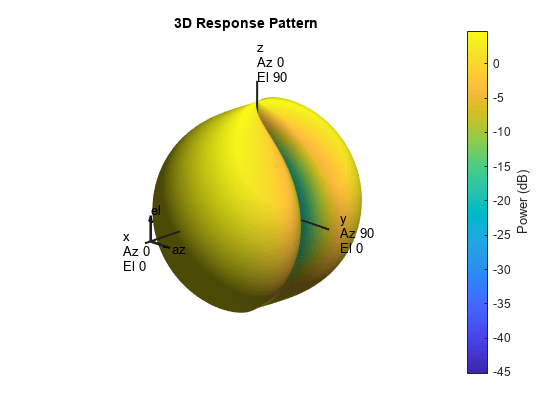
The total response of a crossed-dipole antenna element is a
combination of its frequency response and spatial response. phased.CrossedDipoleAntennaElement calculates
both responses using nearest neighbor interpolation, and then multiplies
the responses to form the total response.
References
[1] Mott, H., Antennas for Radar and Communications, John Wiley & Sons, 1992.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2013a