Three-Winding Nonlinear Transformer
Single-phase nonlinear three-winding transformer
Libraries:
Simscape /
Electrical /
Passive /
Transformers
Description
The Three-Winding Nonlinear Transformer block represents a single-phase, nonlinear, three-winding transformer with a nonideal core. A core may be nonideal due to its magnetic properties or dimensions. This figure shows the equivalent circuit topology,
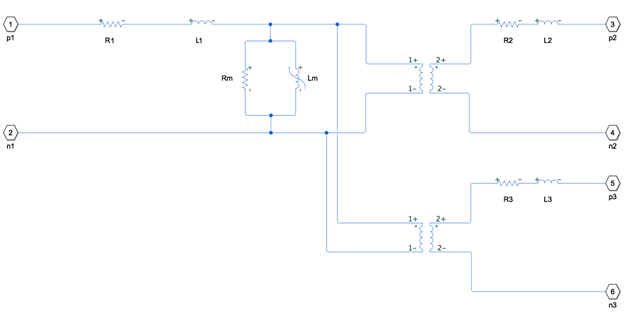
where:
R1 is the primary winding resistance.
L1 is the primary leakage inductance.
R2 is the first secondary winding resistance.
L2 is the first secondary leakage inductance.
R3 is the second secondary winding resistance.
L3 is the second secondary leakage inductance.
Rm is the magnetization resistance.
Lm is the magnetization inductance.
To parameterize the nonlinear magnetization inductance, set the Magnetization inductance parameterized by parameter to one of these options:
Single inductance (linear)Single saturation pointMagnetic flux versus current characteristicMagnetic flux density versus magnetic field strength characteristicMagnetic flux density versus magnetic field strength characteristic with hysteresis
For more information about these parameterization options including the equations that the block uses to model nonlinear magnetization inductance, see the Nonlinear Inductor block reference page.
Simscape™ and Simscape Electrical™ libraries include several blocks than can model the same type of transformer device. However, these blocks make different modeling assumptions. To choose the right block for your application, you must understand how these assumptions impact the block behavior as a function of frequency. For more information, see Choose Blocks to Model Transformers.
Ports
Conserving
Parameters
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2019b
