Get Started with Polyspace Analysis by Using MATLAB
This tutorial shows how to analyze handwritten C/C++ code by running a Polyspace® analysis from the MATLAB® Command Window or the MATLAB Editor. To analyze code generated from a Simulink® model, see Run Polyspace Analysis on Code Generated from Simulink Model.
Prerequisites
Integrate Polyspace with MATLAB before you run a Polyspace analysis from the MATLAB Command Window. See Integrate Polyspace with MATLAB and Simulink.
Run Polyspace Analysis by Using MATLAB
You analyze handwritten C code by configuring and then starting a Polyspace analysis from the MATLAB Command Window or the MATLAB Editor.
To perform a Polyspace analysis, create a polyspace.Project object,
specify the source files and the analysis options, and then start the
analysis by using this object. To create a polyspace.Project
object, use the function
polyspace.Project.
psPrj = polyspace.Project;
In this tutorial, the handwritten code in the file
numerical.c is analyzed. The file
numerical.c is part of your Polyspace software. This source file and the header files required to
analyze it can be found in the folder
polyspaceroot\polyspace\examples\cxx\Bug_Finder_Example\sourcespolyspaceroot is the location of the Polyspace installation folder in your development environment. Create
the paths to these source and header files by using the function
fullfile.
% Create the Path to source and header files sourceFile = fullfile(polyspaceroot, 'polyspace', ... 'examples', 'cxx', 'Bug_Finder_Example', 'sources', 'numerical.c'); includeFolder = fullfile(polyspaceroot, 'polyspace', ... 'examples', 'cxx', 'Bug_Finder_Example', 'sources');
Associate the source and header files with the psPrj
object.
% Associate the source and header files
psPrj.Configuration.Sources = {sourceFile};
psPrj.Configuration.EnvironmentSettings.IncludeFolders = {includeFolder};
Configure the Polyspace analysis options. For instance, you can specify the compiler for the Polyspace analysis and check for violation of specific coding rules. You can also specify a folder where you store the generated results. For instance, store the results in the folder 'results' in the current working directory.
% Specify target compiler psPrj.Configuration.TargetCompiler.Compiler = 'gnu4.9'; % Enable Mchecking for MISRA C violation psPrj.Configuration.CodingRulesCodeMetrics.EnableMisraC3 = true; psPrj.Configuration.CodingRulesCodeMetrics.MisraC3Subset = 'mandatory'; % Specify results folder psPrj.Configuration.ResultsDir = fullfile(pwd,'results');
pwd contains the path of the current working
directory. For details on configurable Polyspace analysis options, see polyspace.Project.Configuration Properties.Start the Polyspace analysis by using the function
run.
% start BugFinder analysis bfStatus = run(psPrj, 'bugFinder');
bfStatus is set to 0. The Polyspace analysis result consists of a list of Bug Finder defects. To
view a summary of the Bug Finder defects in a MATLAB table, use the function getSummary. For
more details about obtaining summary of different kinds of results, see
getSummary.
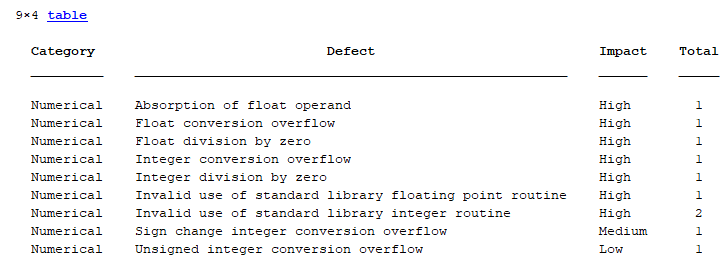
% Obtain list of Bug Finder defects resObj = psPrj.Results; bfSummary = getSummary(resObj, 'defects');
9x4 table
bfSummary.
Frequently Used MATLAB Functions
This table lists some MATLAB functions that you can use for automating a Polyspace analysis from the MATLAB Editor or Command Window.
| Function | Application |
|---|---|
fopen | Opens a file for binary read access. For instance, use this function to read an error log file. |
fclose | Closes a file that was opened by using fopen. For
instance, use this function to close an error log file after
reading it. |
open | Opens a file outside MATLAB in an appropriate application. For instance, use
this function to open psprj files in the
Polyspace UI. |
exist | Checks for the existence of an entity. For instance, use this function to check if a particular folder or file already exists. |
delete | Deletes a file or an object. For instance, use this function to delete older results or unnecessary options objects. |
questdlg | Creates a configurable dialog box. Use this function to change different settings of a Polyspace analysis in a script. For instance, you can choose to enable different coding rules based on the output of this function. |
clear | Clears the workspace by deleting all objects. You can this function at the beginning of the Polyspace analysis. |
clc | Clears all text from the MATLAB Command Window. |
fullfile | Builds full file names from its parts. For instance, use this function to construct the full paths to source files. |
char | Converts an array to a character array. For instance, use this function to construct the input arguments to functions that take character arrays. |
string | Converts a variable into string arrays. For instance, use this function to construct input arguments for functions that take strings. |
dir | Lists the content of the current working folder. For instance, use this function to find specific files or folders in the current folder. |
system | Executes operating system commands and returns their outputs. For instance, use this function to execute a command-line script without exiting MATLAB. |
disp | Displays the value of the input variable. For instance, use
this function for debugging code, similar to how
printf() is used in C code. |
visdiff | Compares two files or folder. For instance, use this function to compare results from different Polyspace analysis to see the difference. |
ismember | Determines if the elements in one array are also present in another array. For instance, use this function to check if a checker or coding rule is enabled in a Polyspace analysis, or to filter results to find a specific check. |
any | Determines if any array elements are nonzero. For instance, use this function to check for new results. |
nnz | Returns the number of nonzero matrix elements. For instance, use this function to check for new results. |
fieldnames | Reads a structure, a Java® object, or a Microsoft® COM object and returns the field names. For instance, use this function to read and manipulate tables. |
See Also
polyspace.Project | polyspaceCodeProver | run | run