encode
Syntax
Description
encodedValues = encode(bpsObj,environment)bpsEncoder object.
[
additionally returns the nearest object point for each basis point. The object points are
points that are located on the occupied areas in the input map environment.encodedValues,nearestPoints] = encode(bpsObj,environment)
Examples
Load an example map into the workspace, and use it to create an occupancy map with a resolution of 10 cells/meter.
load("exampleMaps.mat","simpleMap"); map = occupancyMap(simpleMap,10);
Specify the basis point set arrangement for encoding as "rectangular-grid".
arrangement = "rectangular-grid";Specify the encoding size as [10 10]. Therefore, the number of basis points returned for encoding the map environment will be 100.
encodingSize = [10 10];
Specify the dimensions of the rectangular grid. For correct results, the dimensions of the rectangular grid must be approximately same as that of the input environment.
xLims = map.XLocalLimits; yLims = map.YLocalLimits; dims = [(xLims(2) - xLims(1)) (yLims(2) - yLims(1))];
Specify the center of the map as the center of the rectangular grid.
center = [sum(xLims)/2 sum(yLims)/2];
Create a basis point set encoder using bpsEncoder object. This object computes the basis points and stores them in the Points property.
bpsObj= bpsEncoder(arrangement,encodingSize,Center=center,Dimensions=dims); basisPoints = bpsObj.Points;
Encode the input 2D map environment by using the encode function.
[encodedValues,nearestPoint] = encode(bpsObj,map);
Display the map and the basis points along with its nearest object points.
show(map) hold on scatter(basisPoints(:,1),basisPoints(:,2),"filled",DisplayName="Basis Points") quiver(basisPoints(:,1),basisPoints(:,2),nearestPoint(:,1)-basisPoints(:,1),... nearestPoint(:,2)-basisPoints(:,2),0,Color='black',DisplayName='Nearest points') legend(Location="bestoutside")
![Figure contains an axes object. The axes object with title Occupancy Grid, xlabel X [meters], ylabel Y [meters] contains 3 objects of type image, scatter, quiver. These objects represent Basis Points, Nearest points.](../../examples/nav_robotics/win64/Encode2DMapEnvironmentUsingBasisPointSetsExample_01.png)
Create a 3-D environment with obstacles by using collision geometry objects such as collisionBox.
center = [0 0 0]; sph1 = collisionSphere(.1); loc1 = [0 0 0] + center; sph1.Pose = se3([0 0 0],"eul","XYZ",loc1); mesh1 = collisionMesh(rand(10,3)); loc2 = [1 0 0] + center; mesh1.Pose = se3([pi/4 0 0],"eul","XYZ",loc2); box1 = collisionBox(.5,.5,.5); loc3 = [0 0 1] + center; box1.Pose = se3([0 0 0],"eul","XYZ",loc3); cylinder1 = collisionCylinder(.2,.5); loc4 = [0 0 -1] + center; cylinder1.Pose = se3([0 pi/4 0],"eul","XYZ",loc4); capsule1 = collisionCapsule(.2,.5); loc5 = [0 1.5 0] + center; capsule1.Pose = se3([0 0 pi/2],"eul","XYZ",loc5); simpleGeom = {sph1,mesh1,box1,cylinder1,capsule1};
Plot the 3-D environment.
figure light; grid on; axis("equal"); view(45,45); hold on; for i=1:length(simpleGeom) show(simpleGeom{i}); end
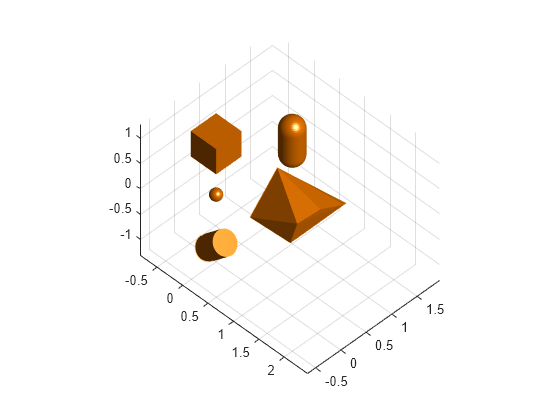
Convert the collision geometry objects to a geometry mesh structure.
meshArray = geom2struct(simpleGeom);
Compute truncated signed distance field (TSDF) map to get voxel-based representation of the 3D environment.
meshTSDFObj = meshtsdf(meshArray,FillInterior=true,Resolution=20)
meshTSDFObj =
meshtsdf with properties:
MeshID: [5×1 double]
NumMesh: 5
MapLimits: [2×3 double]
NumActiveVoxel: 14997
Resolution: 20
TruncationDistance: 0.1500
FillInterior: 1
Encode the TSDF map using the basis point set approach.
arrangement = "uniform-ball-3d";
encodingSize = 100;
bpsObj= bpsEncoder(arrangement,encodingSize,Center=[0 0 0],Radius=2);
basisPoints = bpsObj.Points;
[encoding, nearestPts] = encode(bpsObj,meshTSDFObj);Display the basis points and the nearest object points that represent the obstacles in the environment.
plot3(basisPoints(:,1),basisPoints(:,2),basisPoints(:,3),plannerLineSpec.state{:});
nearestSpec = plannerLineSpec.state(Color='#A2142F',MarkerFaceColor='#A2142F',MarkerEdgeColor='#A2142F');
plot3(nearestPts(:,1),nearestPts(:,2),nearestPts(:,3),nearestSpec{:});
quiver3(basisPoints(:,1),basisPoints(:,2),basisPoints(:,3),...
nearestPts(:,1)-basisPoints(:,1),nearestPts(:,2)-basisPoints(:,2),nearestPts(:,3)-basisPoints(:,3),0,Color='black');
legend('','','','','','Basis points','Nearest object points',Location="southoutside")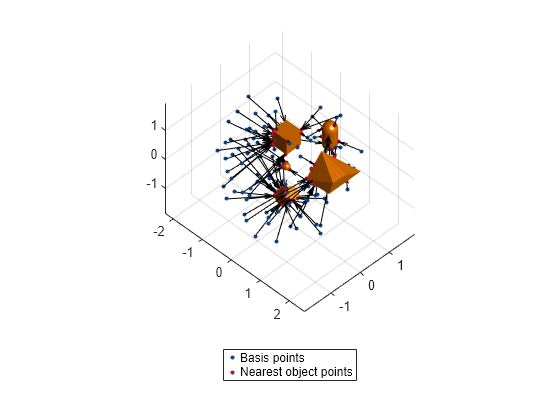
Create a random environment with spherical obstacles.
Specify the number of spherical obstacles to add as 10. Set the range for randomly computing the radius and position values of the spheres.
numSpheres = 10; radRange = [.2 1]; posRange = [0 5]; collisionSpheres = cell(1,numSpheres); spheres = zeros(4,numSpheres); for i=1:numSpheres % Compute radius randomRad = (radRange(2)-radRange(1))*rand(1) + radRange(1); % Compute position randomPos = arrayfun(@(~)(posRange(2)-posRange(1))*rand(1) + posRange(1),1:3); % Create random sphere sph = collisionSphere(randomRad); % Convert coordinates to homogeneous transformation matrix sph.Pose = trvec2tform(randomPos); % Obtain and store its 3D vertices collisionSpheres{i} = sph; % Store its radius and position values spheres(:,i) = [randomRad;randomPos']; end
Display the environment containing spherical obstacles using a helper function.
figure hold on; helperDisplay(collisionSpheres); xlabel("x") ylabel("y") zlabel("z") hold off
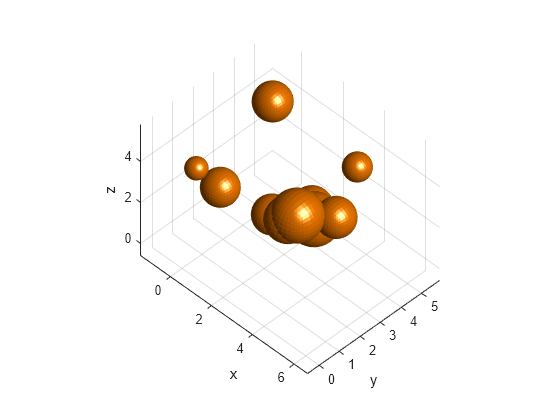
Create a basis point set encoder object for a "uniform-ball-3d" arrangement by specifying the encoding size, radius, and center.
bpsObj = bpsEncoder("uniform-ball-3d",200,Radius=5,Center=[2.5 2.5 2.5]);Encode the environment.
[encoding,nearestPoint] = encode(bpsObj,spheres);
Display results.
figure hold on; helperDisplay(collisionSpheres); basis = bpsObj.Points; plot3(basis(:,1), basis(:,2),basis(:,3), plannerLineSpec.state{:}, DisplayName='Basis Points') nearestSpec = plannerLineSpec.state(Color='#A2142F', MarkerFaceColor='#A2142F', MarkerEdgeColor='#A2142F'); plot3(nearestPoint(:,1), nearestPoint(:,2), nearestPoint(:,3), nearestSpec{:}, DisplayName="nearest obstacles"); quiver3(basis(:,1), basis(:,2),basis(:,3), nearestPoint(:,1)-basis(:,1), ... nearestPoint(:,2)-basis(:,2), nearestPoint(:,3)-basis(:,3),0, Color='black') xlabel("x") ylabel("y") zlabel("z") hold off
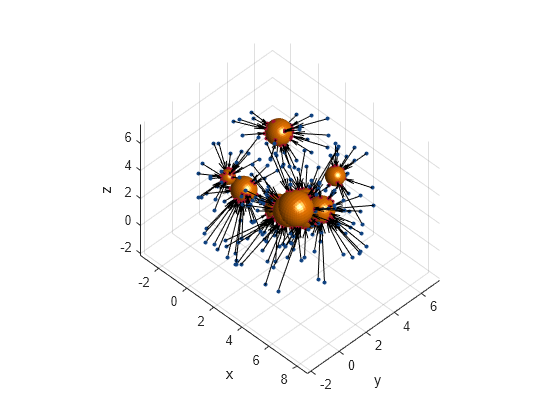
Helper function to display the environment
function helperDisplay(collisionSpheres) light; grid on; axis("equal"); view(45,45); hold on; numSpheres = width(collisionSpheres); for i=1:numSpheres % Show mesh show(collisionSpheres{i}) end end
Input Arguments
Basis point set encoder, specified as a bpsEncoder object.
Input environment to be encoded, specified as a occupancyMap (Navigation Toolbox), binaryOccupancyMap (Navigation Toolbox), meshtsdf (Navigation Toolbox) object,
or a 4-by-M matrix representing spherical obstacles in a 3-D
environment. Each column in the matrix is of the form [r;
x; y; z].
r is the radius of the sphere and [x
y
z] denote the center of the sphere. M is the
number of spherical obstacles in the input environment.
Output Arguments
Distance from each basis point to its nearest object point, returned as a N-by-1 vector.
N is the number of basis points. This value is determined by the
EncodingSize property of the BPS encoder object. The distance
values provide a compact representation of the input map environment for motion planning
with deep learning approaches such as the motion planning networks (MPNet) and
deep-learning-based Covariant Hamiltonian Optimization for Motion Planning
(CHOMP).
For information about MPNet, see Get Started with Motion Planning Networks (Navigation Toolbox). For information about
deep-learning-based CHOMP, see dlCHOMP.
Data Types: double
Nearest object points of each basis point, returned as a N-by-1 vector. Nearest object points are the points on the occupied areas (obstacles) in the input environment.
Data Types: double
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2024a
See Also
bpsEncoder | mpnetSE2 (Navigation Toolbox) | mpnetPrepareData (Navigation Toolbox) | dlCHOMP
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)