Aplicaciones generales
Simulink® permite modelar y simular una amplia gama de sistemas dinámicos. Estos modelos de ejemplo ilustran una variedad de aplicaciones generales, desde las más sencillas hasta las más complejas.
Ejemplos destacados
Simulation of Bouncing Ball
Uses two models of a bouncing ball to show different approaches to modeling hybrid dynamic systems with Zeno behavior. Zeno behavior is informally characterized by an infinite number of events occurring in a finite time interval for certain hybrid systems. As the ball loses energy, the ball collides with the ground in successively smaller intervals of time.
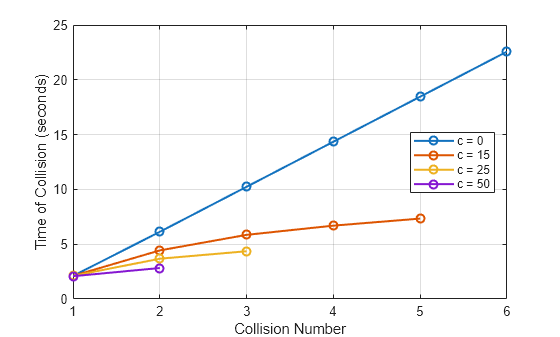
Analyze Impact of Model Parameters on Bouncing Ball Simulation
Analyzes the impact of the damping coefficient on a mass-spring-damper model of the dynamics of a bouncing ball. After running a simulation using a vectorized parameter value, the example analyzes the effect of varying the parameter by exploring these questions:
Single Hydraulic Cylinder Simulation
Use Simulink® to model a hydraulic cylinder. You can apply these concepts to applications where you need to model hydraulic behavior.
Modelo térmico de una casa
Este ejemplo muestra cómo usar Simulink® para crear el modelo térmico de una casa. Este sistema modela el entorno exterior, las características térmicas y el sistema de calefacción residencial.
Approximating Nonlinear Relationships: Type S Thermocouple
Approximate nonlinear relationships of a type S thermocouple.
Digital Waveform Generation: Approximate a Sine Wave
Design and evaluate a sine wave data table for use in digital waveform synthesis applications in embedded systems and arbitrary waveform generation instruments.
Detección precisa de cruces por cero
En este ejemplo se muestra cómo funciona la detección de cruces por cero en Simulink®. Simulink usa la detección de cruces por cero para simular con precisión un cambio abrupto del modelo o una discontinuidad sin disminuir las unidades de tiempo del solver. Para obtener más información, consulte Zero-Crossing Detection.
Spiral Galaxy Formation Simulation Using MATLAB Function Blocks
Use MATLAB Function blocks to simulate and plot galaxy interactions.
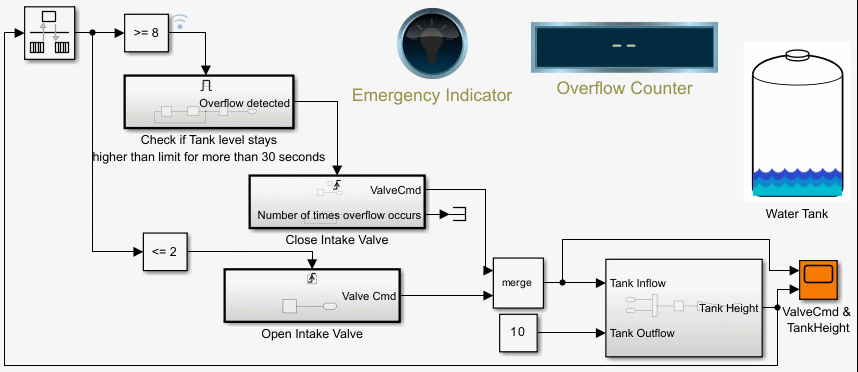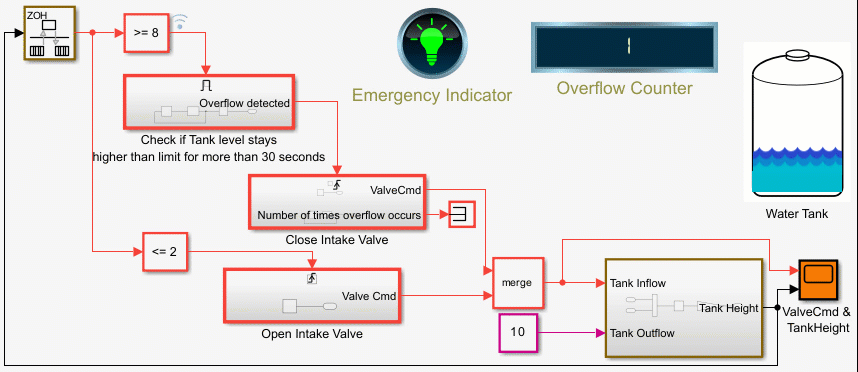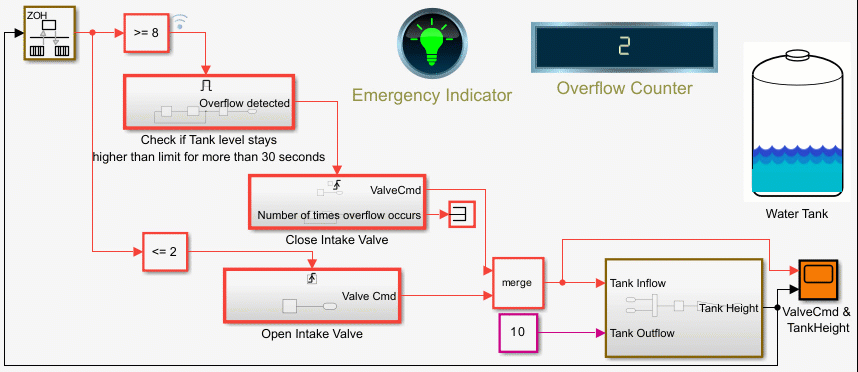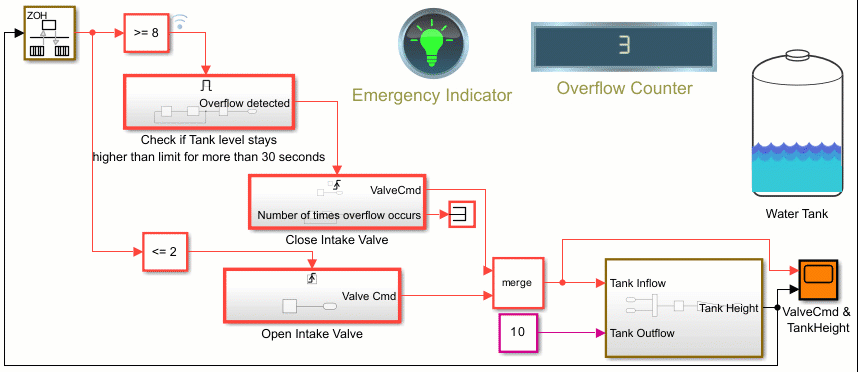
Counters Using Conditionally Executed Subsystems
Implement counters using Enabled and Triggered subsystems. In this example, the model sldemo_counters controls flow of water into a tank and uses a counter to count the number of times overflow occurs, where overflow occurs when the water level in the tank is 8 meters or more for 30 seconds or more.
Modelar la fricción de movimiento slick-slip y los topes rígidos en un sistema de masa-resorte-amortiguador
Este ejemplo muestra cómo incorporar topes rígidos y variaciones en la fricción debidas al movimiento slick-slip en un modelo de masa-resorte-amortiguador.
Controlador de encendido/apagado usando lógica temporal
Este ejemplo muestra cómo usar Stateflow® para modelar el sistema de control de temperatura de encendido/apagado de un calentador. La dinámica del calentador se modela en Simulink®.
Péndulo invertido con animación
En este ejemplo se muestra cómo usar Simulink® para modelar y animar un sistema de péndulo invertido. El centro de masa de un péndulo invertido se encuentra por encima de su punto de rotación. Para mantener esta posición estable, el sistema implementa lógica de control para mover el punto de rotación por debajo del centro de masa en el momento en que el péndulo comienza a caer. El péndulo invertido es un problema de dinámica clásico que se utiliza para probar estrategias de control.
Sistema de doble masa-resorte
Este ejemplo muestra cómo modelar un sistema de doble masa-resorte-amortiguador con una función de fuerza periódica variante. El modelo utiliza un bloque S-Function para animar el sistema de masa durante la simulación. En el sistema, el único sensor está unido a la masa a la izquierda y el actuador está unido a la masa a la izquierda. El ejemplo utiliza una estimación de estado y un control de regulador lineal cuadrático (LQR).
Llenado y vaciado de depósitos con animación
Este ejemplo muestra cómo modelar la dinámica del líquido en un depósito. La animación proporciona una visualización gráfica del depósito a medida que se vacía y se rellena, en función de los parámetros del depósito. Cuando hace clic en START SIM, el depósito se llena y se vacía. Cuando la simulación termine, revise la gráfica que muestra la altura del líquido y los estados de las dos válvulas.
Simulating Systems with Variable Transport Delay Phenomena
Two cases where you can use Simulink® to model variable transport delay phenomena.
Foucault Pendulum Model
Model a Foucault pendulum. The Foucault pendulum was the brainchild of the French physicist Leon Foucault. It was intended to prove that Earth rotates around its axis. The oscillation plane of a Foucault pendulum rotates throughout the day as a result of axial rotation of the Earth. The plane of oscillation completes a whole circle in a time interval T, which depends on the geographical latitude.
Foucault Pendulum Model with Simulink 3D Animation
Animate the Foucault Pendulum Model in the Simulink® 3D Animation™ environment. You can modify the pendulum location by changing the Latitude constant values in the model and other parameters in MATLAB® workspace.
Explore Variable-Step Solvers with Stiff Model
The behavior of variable-step solvers in a Foucault pendulum model. Simulink® solvers ode45, ode15s, ode23, and ode23t are used as test cases. Stiff differential equations are used to solve this problem. There is no exact definition of stiffness for equations. Some numerical methods are unstable when used to solve stiff equations and very small step sizes are required to obtain a numerically stable solution to a stiff problem. A stiff problem may have a fast changing component and a slow changing component.
Exploring the Solver Jacobian Structure of a Model
The example shows how to use Simulink® to explore the solver Jacobian sparsity pattern, and the connection between the solver Jacobian sparsity pattern and the dependency between components of a physical system. A Simulink model that models the synchronization of three metronomes placed on a free moving base are used.
Double Bouncing Ball: Use of Adaptive Zero-Crossing Location
Choose the correct zero-crossing location algorithm, based on the system dynamics. For Zeno dynamic systems, or systems with strong chattering, you can select the adaptive zero-crossing detection algorithm through the Configure pane:
Four Hydraulic Cylinder Simulation
Use Simulink to create a model with four hydraulic cylinders. The model has a single pump and four actuators.
Two Cylinder Model with Load Constraints
Use Simulink to model a rigid rod supporting a large mass interconnecting two hydraulic actuators. This model eliminates the springs as it applies the piston forces directly to the load.
Power Analysis of Spring-Mass-Damper System
Analyze mechanical power of mass-spring damper system.
Van der Pol Oscillator
Model the second-order Van der Pol (VDP) differential equation in Simulink®. In dynamics, the VDP oscillator is non-conservative and has nonlinear damping. At high amplitudes, the oscillator dissipates energy. At low amplitudes, the oscillator generates energy. The oscillator is given by this second-order differential equation:
Collision Avoidance and Trajectory Tracking of a Marine Vessel
Follow a pre-defined trajectory and avoid collisions.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)